Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory T cells in giant cell arteritis
- PMID: 27663755
- PMCID: PMC5639893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2016.07.005
Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory T cells in giant cell arteritis
Abstract
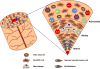
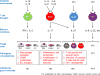
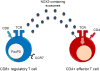
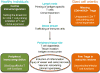
Giant cell arteritis is an autoimmune disease defined by explicit tissue tropism to the walls of medium and large arteries. Pathognomic inflammatory lesions are granulomatous in nature, emphasizing the functional role of CD4T cells and macrophages. Evidence for a pathogenic role of antibodies and immune complexes is missing. Analysis of T cell populations in giant cell arteritis, both in the tissue lesions and in the circulation, has supported a model of broad, polyclonal T cell activation, involving an array of functional T cell lineages. The signature of T cell cytokines produced by vasculitic lesions is typically multifunctional, including IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-21, and GM-CSF, supportive for a general defect in T cell regulation. Recent data describing the lack of a lymph node-based population of anti-inflammatory T cells in giant cell arteritis patients offers a fresh look at the immunopathology of this vasculitis. Due to defective CD8+NOX2+ regulatory T cells, giant cell arteritis patients appear unable to curtail clonal expansion within the CD4T cell compartment, resulting in widespread CD4T cell hyperimmunity. Why unopposed expansion of committed CD4 effector T cells would lead to invasion of the walls of medium and large arteries needs to be explored in further investigations.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory T cells; CD8(+) Treg cells; Giant cell arteritis; Macrophage; Pro-inflammatory T cells.
Copyright © 2016 Société française de rhumatologie. Published by Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint dysfunction in large and medium vessel vasculitis.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 May 1;312(5):H1052-H1059. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00024.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28314758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-gamma-producing T cells in giant cell vasculitis represent a minority of tissue-infiltrating cells and are located distant from the site of pathology.Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):1925-33. Am J Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8669478 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct vascular lesions in giant cell arteritis share identical T cell clonotypes.J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):951-60. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.951. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 8113687 Free PMC article.
-
Giant cell vasculitis is a T cell-dependent disease.Mol Med. 1997 Aug;3(8):530-43. Mol Med. 1997. PMID: 9307981 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis: new insight into the implication of CD161+ T cells.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013 Jan-Feb;31(1 Suppl 75):S65-73. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23663684 Review.
Cited by
-
Vasculitogenic T Cells in Large Vessel Vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 15;13:923582. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.923582. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35784327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Application of Exosomes in Inflammatory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 24;22(3):1144. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031144. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giant Cell Arteritis: Practical Pearls and Updates.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018 Jan 17;22(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11916-018-0655-y. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018. PMID: 29344777 Review.
-
Clinical and pathological evolution of giant cell arteritis: a prospective study of follow-up temporal artery biopsies in 40 treated patients.Mod Pathol. 2017 Jun;30(6):788-796. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.10. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Mod Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28256573 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint dysfunction in large and medium vessel vasculitis.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 May 1;312(5):H1052-H1059. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00024.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28314758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

