c-Rel is dispensable for the differentiation and functional maturation of M cells in the follicle-associated epithelium
- PMID: 27663963
- PMCID: PMC5152706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.09.008
c-Rel is dispensable for the differentiation and functional maturation of M cells in the follicle-associated epithelium
Abstract
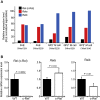
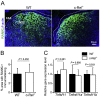
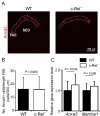
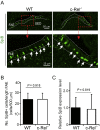
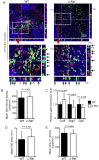
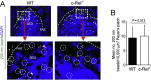
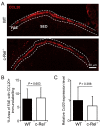
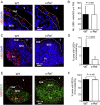
M cells reside within the follicle-associated epithelium (FAE) overlying the gut-associated lymphoid tissues. These unique phagocytic epithelial cells enable the mucosal immune system to sample antigens within the lumen of the intestine. The differentiation of M cells from uncommitted precursors in the FAE is dependent on the production of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) by subepithelial stromal cells. The ligation of a variety of cell surface receptors activates the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) family of transcription factors which in-turn induce the transcription of multiple target genes. RANKL-stimulation can stimulate the nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit c-Rel. We therefore used c-Rel-deficient mice to determine whether the differentiation and functional maturation of M cells in the Peyer's patches was dependent on c-Rel. Our data show that c-Rel-deficiency does not influence the expression of RANKL or RANK in Peyer's patches, or the induction of M-cell differentiation in the FAE. RANKL-stimulation in the differentiating M cells induces the expression of SpiB which is essential for their subsequent maturation. However, SpiB expression in the FAE was also unaffected in the absence of c-Rel. As a consequence, the functional maturation of M cells was not impaired in the Peyer's patches of c-Rel-deficient mice. Although our data showed that the specific expression of CCL20 and ubiquitin D in the FAE was not impeded in the absence of c-Rel, the expression of ubiquitin D was dramatically reduced in the B cell-follicles of c-Rel-deficient mice. Coincident with this, we also observed that the status of follicular dendritic cells in the B cell-follicles was dramatically reduced in Peyer's patches from c-Rel-deficient mice. Taken together, our data show that c-Rel is dispensable for the RANKL-mediated differentiation and functional maturation of M cells.
Keywords: Follicle-associated epithelium; M cells; Peyer’s patches; RANKL; c-Rel.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell culture modeling of specialized tissue: identification of genes expressed specifically by follicle-associated epithelium of Peyer's patch by expression profiling of Caco-2/Raji co-cultures.Int Immunol. 2004 Jan;16(1):91-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh011. Int Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14688064
-
The functional maturation of M cells is dramatically reduced in the Peyer's patches of aged mice.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Sep;6(5):1027-37. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.141. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23360902 Free PMC article.
-
Development of intestinal M cells and follicle-associated epithelium is regulated by TRAF6-mediated NF-κB signaling.J Exp Med. 2018 Feb 5;215(2):501-519. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160659. Epub 2018 Jan 16. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29339448 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Peyer's patches, follicle-associated epithelium and M cell: lessons from immunodeficient and knockout mice.Semin Immunol. 1999 Jun;11(3):183-91. doi: 10.1006/smim.1999.0174. Semin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10381864 Review.
-
Molecular insights into the mechanisms of M-cell differentiation and transcytosis in the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues.Anat Sci Int. 2018 Jan;93(1):23-34. doi: 10.1007/s12565-017-0418-6. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Anat Sci Int. 2018. PMID: 29098649 Review.
Cited by
-
M cell-dependent antigen uptake on follicle-associated epithelium for mucosal immune surveillance.Inflamm Regen. 2018 Sep 3;38:15. doi: 10.1186/s41232-018-0072-y. eCollection 2018. Inflamm Regen. 2018. PMID: 30186536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M Cells: Intelligent Engineering of Mucosal Immune Surveillance.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 2;10:1499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01499. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31312204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging-Related Impairments to M Cells in Peyer's Patches Coincide With Disturbances to Paneth Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 6;12:761949. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761949. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34938288 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Intestinal M Cells on Intestinal Barrier and Neuropathological Properties in an AD Mouse Model.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Dec;61(12):10006-10022. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03807-9. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38066398
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/J014672/1/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004227/1/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/D/20231762/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J01446X/1/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

