Comparison of illegal drug use pattern in Taiwan and Korea from 2006 to 2014
- PMID: 27663984
- PMCID: PMC5034652
- DOI: 10.1186/s13011-016-0078-x
Comparison of illegal drug use pattern in Taiwan and Korea from 2006 to 2014
Abstract
Background: Illegal drug use has long been a global concern. Taiwan and Korea are geographically adjacent and both countries have experienced the illegal use problems of methamphetamine, a predominant prototype of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS). NPS, a term coined by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in recent years, have not been scrutinized for their safety and may become a new threat to public health and security worldwide. To conduct evidence-based drug policy, it is imperative to estimate the trend and pattern of illegal drug use. Therefore, this study aims to analyze and compare the current status of drug-related seizures, arrests and illegal drug use, with a focus on methamphetamine and NPS, between Taiwan and Korea.
Methods: Data of illegal drug (including NPS)-related seizures and arrests were collected via anti-drug related agencies of both countries from 2006 through 2014.Since listing of NPS as controlled substances was a result of NPS abuse liability through official evaluation, the items of controlled NPS were used as an indicator of emerging use. These data obtained from Taiwan and Korea was then compared.
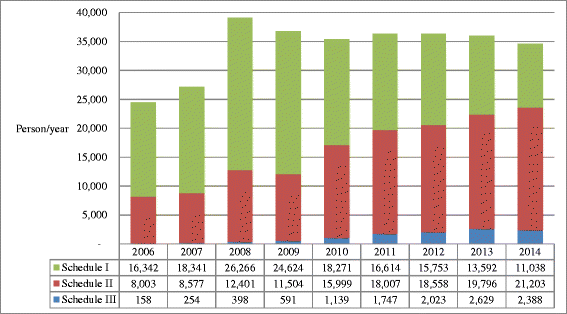
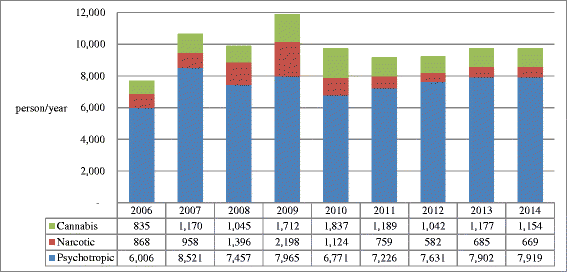
Results: The results showed that while methamphetamine remained as a predominant drug in both Taiwan and Korea for decades, different illegal drug use patterns have been observed in these two countries. In Taiwan, the major illegal drugs were methamphetamine, heroin, and ketamine, whereas in Korea those were methamphetamine and cannabis. By comparison of per capita illicit drug seizures, the illegal drug use situation in Taiwan was at a higher stake than that in Korea. In terms of NPS use, ketamine has been a major drug in Taiwan, but it was seldom found in Korea. Besides ketamine, the major type of NPS was synthetic cathinones in Taiwan whereas it was synthetic cannabinoids and phenethylamines in Korea. The difference in the numbers of controlled NPS items between Taiwan (23) and Korea (93) may be due to the implementation of temporary control on NPS in Korea since 2011.
Conclusion: While the problem of methamphetamine still lingers, NPS have emerged as a new issue in both countries. However, the NPS pattern was different between Taiwan and Korea. Although the controlled NPS items in Taiwan were far less than those in Korea, the quantity of total NPS seizures, especially with ketamine, was much larger in Taiwan than in Korea. Different NPS pattern may also imply they were from different sources. Factors other than geographical proximity, such as drug policy and availability and accessibility to drugs, should be taken into account for the current status of illegal drug use in Korea and Taiwan.
Keywords: Drug seizures; Ketamine; Korea; Methamphetamine; New Psychoactive Substances (NPS); Taiwan.
Figures
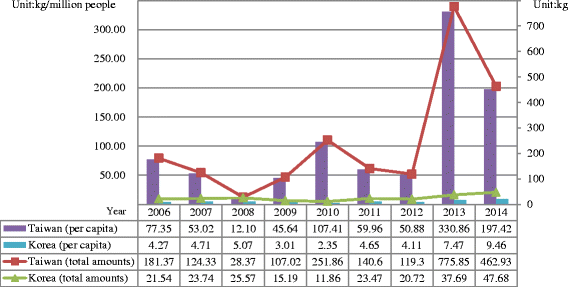
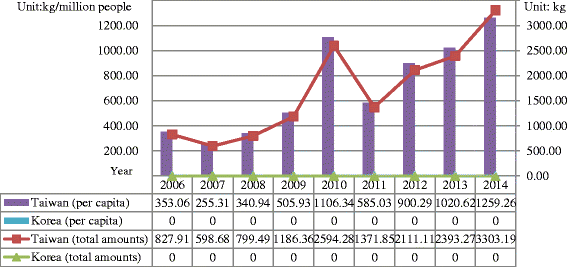
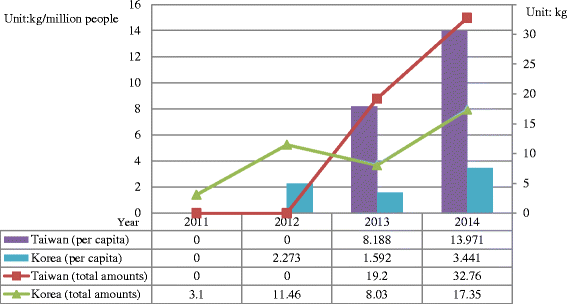
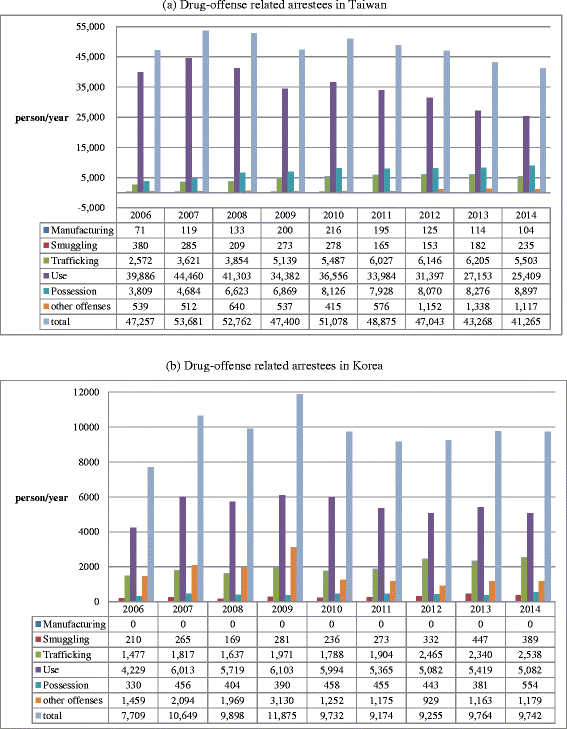
Similar articles
-
New psychoactive substances in Taiwan: challenges and strategies.Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2020 Jul;33(4):306-311. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000604. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32167950 Review.
-
Comparison of legislative management for new psychoactive substances control among Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Feb;36(2):135-142. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12140. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31643137 Free PMC article.
-
New psychoactive substances in Taiwan: The current situation and initiative for rational scheduling.J Food Drug Anal. 2021 Mar 15;29(1):168-181. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3225. J Food Drug Anal. 2021. PMID: 35696229 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of new psychoactive substances in Northeast Asia from 2007 to 2015.Forensic Sci Int. 2017 Mar;272:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Forensic Sci Int. 2017. PMID: 28088088
-
New psychoactive substances of natural origin: A brief review.J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Jul;25(3):461-471. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Food Drug Anal. 2017. PMID: 28911631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and patterns of illicit drug use in people with human immunodeficiency virus infection in Korea.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 1;16(4):e0249361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249361. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33793637 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing Opioid-Related Chemical Coping in Long-Term Opioid Therapy for Chronic Noncancer Pain: A Multicenter, Observational, Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2018 Oct 14;7(10):354. doi: 10.3390/jcm7100354. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30322212 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal profile of illicit drug consumption in Guangzhou, China monitored by wastewater-based epidemiology.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Aug;26(23):23593-23602. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05575-3. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31203544
-
Cognitive profile of ketamine-dependent patients compared with methamphetamine-dependent patients and healthy controls.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Jul;235(7):2113-2121. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4910-z. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29713787
-
Decreased Blood Levels of Oxytocin in Ketamine-Dependent Patients During Early Abstinence.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 26;9:633. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00633. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30534093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. 1961.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Convention on Psychotropic Substances. 1971.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. 1988.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2015. 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

