Interventions to Improve Adolescent Nutrition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27664593
- PMCID: PMC5026685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.06.022
Interventions to Improve Adolescent Nutrition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
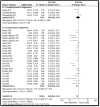
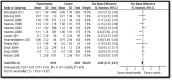
Adequate adolescent nutrition is an important step for optimal growth and development. In this article, we systematically reviewed published studies till December 2014 to ascertain the effectiveness of interventions to improve adolescent nutrition. We found one existing systematic review on interventions to prevent obesity which we updated and conducted de novo reviews for micronutrient supplementation and nutrition interventions for pregnant adolescents. Our review findings suggest that micronutrient supplementation among adolescents (predominantly females) can significantly decrease anemia prevalence (relative risk [RR]: .69; 95% confidence interval [CI]: .62-.76) while interventions to improve nutritional status among "pregnant adolescents" showed statistically significant improved birth weight (standard mean difference: .25; 95% CI: .08-.41), decreased low birth weight (RR: .70; 95% CI: .57-.84), and preterm birth (RR: .73; 95% CI: .57-.95). Interventions to promote nutrition and prevent obesity had a marginal impact on reducing body mass index (standard mean difference: -.08; 95% CI: -.17 to .01). However, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to significant statistical heterogeneity.
Keywords: Adolescent nutrition; Micronutrient supplementation; Preconception nutrition; Pregnant adolescents.
Copyright © 2016 Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Story M. Nutritional requirements during adolescence. In: McAnarney E.R., Kreipe R.E., Orr D.E., Comerci G.D., editors. Textbook of adolescent medicine. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia: 1992. pp. 75–84.
-
- Black R.E., Victora C.G., Walker S.P. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013;382:427–451. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . WHO; Geneva: 2012. Adolescent pregnancy.
-
- Rokholm B., Baker J.L., Sørensen T.I.A. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999—a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes Rev. 2010;11:835–846. - PubMed
-
- Nichols M.S., de Silva-Sanigorski A.M., Cleary J.E. Decreasing trends in overweight and obesity among an Australian population of preschool children. Int J Obes. 2011;35:916–924. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

