Ad E1A 243R oncoprotein promotes association of proto-oncogene product MYC with the NuA4/Tip60 complex via the E1A N-terminal repression domain
- PMID: 27664947
- PMCID: PMC5109832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.09.005
Ad E1A 243R oncoprotein promotes association of proto-oncogene product MYC with the NuA4/Tip60 complex via the E1A N-terminal repression domain
Abstract
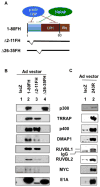
The adenovirus E1A 243R oncoprotein targets TRRAP, a scaffold protein that assembles histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complexes, such as the NuA4/Tip60 complex which mediates transcriptional activity of the proto-oncogene MYC and helps determine the cancer cell phenotype. How E1A transforms cells through TRRAP remains obscure. We performed proteomic analysis with the N-terminal transcriptional repression domain of E1A 243R (E1A 1-80) and showed that E1A 1-80 interacts with TRRAP, p400, and three other members of the NuA4 complex - DMAP1, RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 - not previously shown to associate with E1A 243R. E1A 1-80 interacts with these NuA4 components and MYC through the E1A TRRAP-targeting domain. E1A 243R association with the NuA4 complex was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation and analysis with DMAP1, Tip60, and MYC. Significantly, E1A 243R promotes association of MYC/MAX with the NuA4/Tip60 complex, implicating the importance of the MYC/NuA4 pathway in cellular transformation by both MYC and E1A.
Keywords: 243R; DMAP1; E1A 1-80; NuA4; RUVBL1; RUVBL2; TRRAP; Tip60.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Berk AJ. Recent lessons in gene expression, cell cycle control, and cell biology from adenovirus. Oncogene. 2005;24:7673–7685. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty AA, Tansey WP. Adenoviral E1A function through Myc. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6–9. - PubMed
-
- Cowling VH, Cole MD. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by the Myc oncoproteins. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:242–252. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

