Determinants of longitudinal health-related quality-of-life change in children with asthma from low-income families: a report from the PROMIS® Pediatric Asthma Study
- PMID: 27664979
- PMCID: PMC5330944
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12827
Determinants of longitudinal health-related quality-of-life change in children with asthma from low-income families: a report from the PROMIS® Pediatric Asthma Study
Abstract
Background: How the longitudinal asthma control status and other socio-demographic factors influence the changes of health-related quality of life (HRQOL) among asthmatic children, especially from low-income families, has not been fully investigated.
Objectives: This study aimed to describe the trajectories of asthma-specific HRQOL over 15 months and examine the effect of asthma control status on HRQOL by taking socio-demographic factors into consideration.
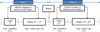
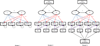
Methods: A total of 229 dyads of asthmatic children and their parents enroled in public insurance programs were recruited for assessing asthma control status and HRQOL over four time points of assessment. Asthma control status was measured using the Asthma Control and Communication Instrument, and asthma-specific HRQOL was assessed using the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System's Pediatric Asthma Impact Scale. Latent growth models (LGMs) were applied to examine the trajectory of HRQOL and the factors contributing to the changes of HRQOL.
Results: Unconditional LGM revealed that HRQOL was improved over time. Conditional LGM suggested that accounting for asthma control and participants' socio-demographic factors, the variation in the initial level of HRQOL was significant, yet the rate of change was not. Conditional LGM also revealed that poorly controlled asthma status was associated with poor HRQOL at each time point (P's < 0.05). Lower parental education was associated with lower baseline HRQOL (P < 0.05). Hispanic children had a larger increase in HRQOL over time (P < 0.01) than non-Hispanic White children.
Conclusions: Vulnerable socio-demographic characteristics and poorly controlled asthma status affect HRQOL in children. This finding encourages interventions to improve asthma control status and HRQOL in minority children.
Keywords: asthma control; children; health-related quality of life; latent growth models; patient-reported outcomes.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No conflicts of interest to all co-authors.
Figures
References
-
- Bloom B, Jones LI, Freeman G. Summary health statistics for U.S. children: National health interview survey, 2012. Vital Health Stat 10. 2013;258:1–81. - PubMed
-
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma-summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:S94–S138. - PubMed
-
- Seid M, Limbers CA, Driscoll KA, Opipari-Arrigan LA, Gelhard LR, Varni JW. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the pediatric quality of life inventory (PedsQL) generic core scales and asthma symptoms scale in vulnerable children with asthma. J Asthma. 2010;47(2):170–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical