Measuring the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: a baseline analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015
- PMID: 27665228
- PMCID: PMC5055583
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31467-2
Measuring the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: a baseline analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2017 Jan 7;389(10064):e1. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32610-1. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28091377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: In September, 2015, the UN General Assembly established the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs specify 17 universal goals, 169 targets, and 230 indicators leading up to 2030. We provide an analysis of 33 health-related SDG indicators based on the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2015 (GBD 2015).
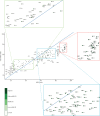
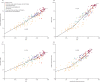
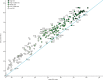
Methods: We applied statistical methods to systematically compiled data to estimate the performance of 33 health-related SDG indicators for 188 countries from 1990 to 2015. We rescaled each indicator on a scale from 0 (worst observed value between 1990 and 2015) to 100 (best observed). Indices representing all 33 health-related SDG indicators (health-related SDG index), health-related SDG indicators included in the Millennium Development Goals (MDG index), and health-related indicators not included in the MDGs (non-MDG index) were computed as the geometric mean of the rescaled indicators by SDG target. We used spline regressions to examine the relations between the Socio-demographic Index (SDI, a summary measure based on average income per person, educational attainment, and total fertility rate) and each of the health-related SDG indicators and indices.
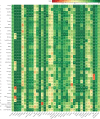
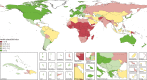
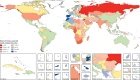
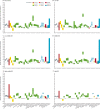
Findings: In 2015, the median health-related SDG index was 59·3 (95% uncertainty interval 56·8-61·8) and varied widely by country, ranging from 85·5 (84·2-86·5) in Iceland to 20·4 (15·4-24·9) in Central African Republic. SDI was a good predictor of the health-related SDG index (r2=0·88) and the MDG index (r2=0·92), whereas the non-MDG index had a weaker relation with SDI (r2=0·79). Between 2000 and 2015, the health-related SDG index improved by a median of 7·9 (IQR 5·0-10·4), and gains on the MDG index (a median change of 10·0 [6·7-13·1]) exceeded that of the non-MDG index (a median change of 5·5 [2·1-8·9]). Since 2000, pronounced progress occurred for indicators such as met need with modern contraception, under-5 mortality, and neonatal mortality, as well as the indicator for universal health coverage tracer interventions. Moderate improvements were found for indicators such as HIV and tuberculosis incidence, minimal changes for hepatitis B incidence took place, and childhood overweight considerably worsened.
Interpretation: GBD provides an independent, comparable avenue for monitoring progress towards the health-related SDGs. Our analysis not only highlights the importance of income, education, and fertility as drivers of health improvement but also emphasises that investments in these areas alone will not be sufficient. Although considerable progress on the health-related MDG indicators has been made, these gains will need to be sustained and, in many cases, accelerated to achieve the ambitious SDG targets. The minimal improvement in or worsening of health-related indicators beyond the MDGs highlight the need for additional resources to effectively address the expanded scope of the health-related SDGs.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Making the SDGs useful: a Herculean task.Lancet. 2016 Oct 8;388(10053):1453-1454. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31635-X. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27665229 No abstract available.
-
Measuring progress towards the SDGs-a new vital science.Lancet. 2016 Oct 8;388(10053):1455-1458. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31791-3. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27733280 No abstract available.
-
The Sustainable Development Goals: ambiguities of accountability.Lancet. 2017 Jan 28;389(10067):365. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30152-6. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28137691 No abstract available.
References
-
- UN . Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. United Nations; New York: 2015. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld (accessed Sept 14, 2015).
-
- IAEG-SDGs . Report of the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on the Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. Economic and Social Council; New York, NY: 2016. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/statcom/47th-session/documents/2016-2-SDGs-Re... (accessed July 15, 2016).
-
- Nilsson M, Griggs D, Visbeck M. Policy: map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature. 2016;534:320–322. - PubMed
-
- International Council for Science. International Social Science Council . Review of targets for the Sustainable Development Goals: the science perspective. International Council for Science; Paris: 2015.
-
- Horton R. Offline: Why the Sustainable Development Goals will fail. Lancet. 2014;383:2196.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 AG032572/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- US/United States/United States
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 ES000260/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 099876/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K010174/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG030153/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG007479/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RP-PG-0407-10184/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R03 AG043052/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR/CS/010/014/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 095066/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/K00669X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

