The role of adenosinergic pathway in human autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 27665459
- PMCID: PMC5126201
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-016-8870-2
The role of adenosinergic pathway in human autoimmune diseases
Abstract
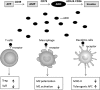
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the abnormal immune response against self-tissue, which are caused by the failure of nature immune homeostasis. Nature immune homeostasis represents the normal state of appropriate immune response to nonself-antigen and unresponsiveness to self-antigens. In normal situation, immune homeostasis is regulated by immunosuppressive signal and immunostimulating signal together. Accumulating data have demonstrated that the adenosinergic pathway played key roles in immune suppression and shield body from an excessive inflammatory response. The deficiency of adenosinergic pathway results in the imbalance between the pro- and anti-inflammatory activities. Thus, researchers pay much attention to the role of adenosinergic pathway in autoimmune diseases development. To date, accumulating data have suggested an important role of adenosinergic pathway-related molecules (i.e., CD39, CD73, ADA, adenosine receptors, etc.) in many types of human autoimmune diseases. More importantly, these findings have presented potential value of adenosinergic pathway analysis to be used for autoimmune diseases diagnosis, monitoring and treatment. In this review, we will provide a comprehensive description of the role of adenosinergic pathway in human autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Adenosine receptor; Adenosinergic pathway; Autoimmune diseases; Immunosuppression.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standard Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Margo CE, Harman LE. Autoimmune disease: conceptual history and contributions of ocular immunology. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

