A Transient Developmental Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gives Rise to Innate-like B and T Cells
- PMID: 27666010
- PMCID: PMC5524382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.08.013
A Transient Developmental Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gives Rise to Innate-like B and T Cells
Abstract
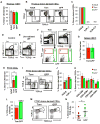
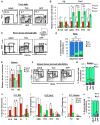
The generation of distinct hematopoietic cell types, including tissue-resident immune cells, distinguishes fetal from adult hematopoiesis. However, the mechanisms underlying differential cell production to generate a layered immune system during hematopoietic development are unclear. Using an irreversible lineage-tracing model, we identify a definitive hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) that supports long-term multilineage reconstitution upon transplantation into adult recipients but does not persist into adulthood in situ. These HSCs are fully multipotent, yet they display both higher lymphoid cell production and greater capacity to generate innate-like B and T lymphocytes as compared to coexisting fetal HSCs and adult HSCs. Thus, these developmentally restricted HSCs (drHSCs) define the origin and generation of early lymphoid cells that play essential roles in establishing self-recognition and tolerance, with important implications for understanding autoimmune disease, allergy, and rejection of transplanted organs.
Keywords: development; hematopoiesis; hematopoietic stem cell; immune cells; innate-like B and T lymphocytes; lineage potential; lineage tracing; self-renewal; tissue resident; transplantation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures
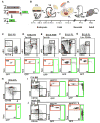
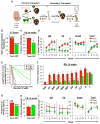

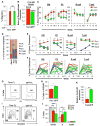
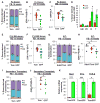
Comment in
-
Fetal to Adult Hematopoiesis with the "Flk" of a Switch.Cell Stem Cell. 2016 Dec 1;19(6):673-674. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.013. Cell Stem Cell. 2016. PMID: 27912084
-
Fetal hematopoietic stem cells are making waves.Stem Cell Investig. 2017 Apr 7;4:25. doi: 10.21037/sci.2017.03.06. eCollection 2017. Stem Cell Investig. 2017. PMID: 28447040 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barber CL, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Dorshkind K. Reduced production of B-1-specified common lymphoid progenitors results in diminished potential of adult marrow to generate B-1 cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(1):3700–13704. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benlagha K, Kyin T, Beavis A, Teyton L, Bendelac A. A thymic precursor to the NK T cell lineage. Science. 2002;296:553–555. - PubMed
-
- Benz C, Copley MR, Kent DG, Wohrer S, Cortes A, Aghaeepour N, Ma E, Mader H, Rowe K, Day C, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell subtypes expand differentially during development and display distinct lymphopoietic programs. Cell stem cell. 2012;10:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bowie MB, Kent DG, Dykstra B, McKnight KD, McCaffrey L, Hoodless PA, Eaves CJ. Identification of a new intrinsically timed developmental checkpoint that reprograms key hematopoietic stem cell properties. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:5878–5882. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

