Trimetazidine protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via effects on cardiac miRNA‑21 expression, Akt and the Bcl‑2/Bax pathway
- PMID: 27666568
- PMCID: PMC5101925
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5773
Trimetazidine protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via effects on cardiac miRNA‑21 expression, Akt and the Bcl‑2/Bax pathway
Abstract
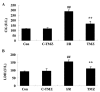
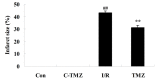
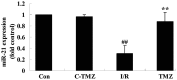
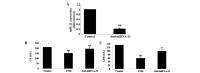
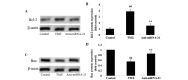
Trimetazidine is a piperazine-derived metabolic agent, which exerts cell protective effects and has been reported to be efficient in the treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris. In addition, it has been shown to exert protection against acute myocardial infarction. The present study aimed to investigate whether trimetazidine protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and to determine whether its curative effects are associated with microRNA (miRNA)‑21 expression, Akt, and the B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2)/Bcl‑2‑associated X protein (Bax) pathway. Cardiac I/R injury was induced by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery in adult rats. Subsequently, cardiac function was evaluated, and the expression levels of miRNA‑21, Bcl‑2, Bax and phosphorylated‑Akt were detected using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The results indicated that trimetazidine was able to significantly protect cardiac function and reduce infarct size in rats following cardiac I/R injury. Furthermore, trimetazidine significantly promoted miRNA‑21 expression and phosphorylated‑Akt protein expression, and reduced the Bcl‑2/Bax ratio in rats following cardiac I/R injury. Knockdown of miRNA‑21 using anti‑miR‑21 plasmids was able to reverse the protective effects of trimetazidine against cardiac I/R injury. These results indicated that miRNA‑21 serves a protective role in cardiac I/R injury via Akt and the Bcl‑2/Bax pathway. In addition, trimetazidine exerts protective effects against cardiac I/R injury through cardiac miRNA‑21 expression, Akt, and the Bcl‑2/Bax pathway. Therefore, the present study provided evidence regarding the protective effects of miRNA‑21 on cardiac I/R injury following treatment with trimetazidine in vivo.
Figures
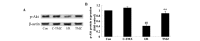

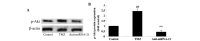
References
-
- Pisarenko OI, Lankin VZ, Konovalova GG, Serebryakova LI, Shulzhenko VS, Timoshin AA, Tskitishvili OV, Pelogeykina YA, Studneva IM. Apelin-12 and its structural analog enhance antioxidant defense in experimental myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;391:241–250. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2008-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu LF, Qin Q, Qian ZH, Shi M, Deng QC, Zhu WP, Zhang H, Tao XM, Liu Y. Protective effects of melatonin on ischemia-reperfusion induced myocardial damage and hemodynamic recovery in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:3681–3686. - PubMed
-
- Lenčová-Popelová O, Jirkovský E, Mazurová Y, Lenčo J, Adamcová M, Šimůnek T, Geršl V, Štěrba M. Molecular remodeling of left and right ventricular myocardium in chronic anthracycline cardiotoxicity and post-treatment follow up. PLoS One. 2014;9:e96055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chua CC, Gao J, Ho YS, Xu X, Kuo IC, Chua KY, Wang H, Hamdy RC, Reed JC, Chua BH. Over-expression of a modified bifunctional apoptosis regulator protects against cardiac injury and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in transgenic mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;81:20–27. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

