Bromodomain Inhibitors Correct Bioenergetic Deficiency Caused by Mitochondrial Disease Complex I Mutations
- PMID: 27666594
- PMCID: PMC5055448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.08.023
Bromodomain Inhibitors Correct Bioenergetic Deficiency Caused by Mitochondrial Disease Complex I Mutations
Abstract
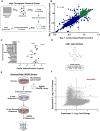
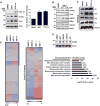
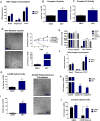
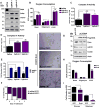
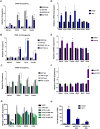
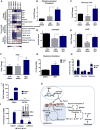
Mitochondrial diseases comprise a heterogeneous group of genetically inherited disorders that cause failures in energetic and metabolic function. Boosting residual oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) activity can partially correct these failures. Herein, using a high-throughput chemical screen, we identified the bromodomain inhibitor I-BET 525762A as one of the top hits that increases COX5a protein levels in complex I (CI) mutant cybrid cells. In parallel, bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), a target of I-BET 525762A, was identified using a genome-wide CRISPR screen to search for genes whose loss of function rescues death of CI-impaired cybrids grown under conditions requiring OXPHOS activity for survival. We show that I-BET525762A or loss of BRD4 remodeled the mitochondrial proteome to increase the levels and activity of OXPHOS protein complexes, leading to rescue of the bioenergetic defects and cell death caused by mutations or chemical inhibition of CI. These studies show that BRD4 inhibition may have therapeutic implications for the treatment of mitochondrial diseases.
Keywords: BRD4; OXPHOS; PGC-1α; bromodomain inhibitors; mitochondria; mitochondrial disorders.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Mitochondrial Diseases: Shortcuts to Therapies and Therapeutic Shortcuts.Mol Cell. 2016 Oct 6;64(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.022. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27716487
References
-
- Bai Y, Hajek P, Chomyn A, Chan E, Seo BB, Matsuno-Yagi A, Yagi T, Attardi G. Lack of complex I activity in human cells carrying a mutation in MtDNA-encoded ND4 subunit is corrected by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae NADH-quinone oxidoreductase (NDI1) gene. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2001;276:38808–38813. - PubMed
-
- Baratta MG, Schinzel AC, Zwang Y, Bandopadhayay P, Bowman-Colin C, Kutt J, Curtis J, Piao H, Wong LC, Kung AL, et al. An in-tumor genetic screen reveals that the BET bromodomain protein, BRD4, is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2015;112:232–237. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

