Identification and comparative analysis of the microRNA transcriptome in roots of two contrasting tobacco genotypes in response to cadmium stress
- PMID: 27667199
- PMCID: PMC5036098
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32805
Identification and comparative analysis of the microRNA transcriptome in roots of two contrasting tobacco genotypes in response to cadmium stress
Abstract
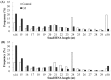
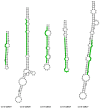
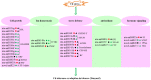
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) is more acclimated to cadmium (Cd) uptake and preferentially enriches Cd in leaves than other crops. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial roles in regulating expression of various stress response genes in plants. However, genome-wide expression of miRNAs and their target genes in response to Cd stress in tobacco are still unknown. Here, miRNA high-throughput sequencing technology was performed using two contrasting tobacco genotypes Guiyan 1 and Yunyan 2 of Cd-sensitive and tolerance. Comprehensive analysis of miRNA expression profiles in control and Cd treated plants identified 72 known (27 families) and 14 novel differentially expressed miRNAs in the two genotypes. Among them, 28 known (14 families) and 5 novel miRNAs were considered as Cd tolerance associated miRNAs, which mainly involved in cell growth, ion homeostasis, stress defense, antioxidant and hormone signaling. Finally, a hypothetical model of Cd tolerance mechanism in Yunyan 2 was presented. Our findings suggest that some miRNAs and their target genes and pathways may play critical roles in Cd tolerance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of cadmium-responsive microRNAs and their target genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) roots.J Exp Bot. 2013 Nov;64(14):4271-87. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert240. Epub 2013 Sep 7. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 24014874 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of chromium stress-responsive micro RNAs and their target genes in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) roots.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015 Nov;34(11):2573-82. doi: 10.1002/etc.3097. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26053264
-
Genome-Wide Identification of MicroRNAs in Response to Cadmium Stress in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) Using High-Throughput Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 10;19(5):1431. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051431. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29748489 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA transcriptome reveals key miRNAs and their targets contributing to the difference in Cd tolerance of two contrasting maize genotypes.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 May;256:114881. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114881. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 37030049
-
MicroRNA-mRNA expression profiles and their potential role in cadmium stress response in Brassica napus.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Dec 19;19(1):570. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2189-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31856702 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Comprehensive Gene Feature, Evolution, and Expression Analysis of Plant Metal Tolerance Proteins in Tobacco Under Heavy Metal Toxicity.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 24;10:345. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00345. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31105736 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of conserved microRNAs during short and prolonged chromium stress in rice (Oryza sativa).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jan;27(1):380-390. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06760-0. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31792790
-
Traversing the Links between Heavy Metal Stress and Plant Signaling.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Feb 5;9:12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00012. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29459874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of the invertase gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) reveals NtNINV10 participating the sugar metabolism.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 2;14:1164296. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1164296. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37332710 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs and their roles in regulating the agronomic traits of crops.Fundam Res. 2023 Mar 17;3(5):718-726. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.02.020. eCollection 2023 Sep. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 38933294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han F. X. et al.. Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere. Naturwissenschaften. 89, 497–504 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Bovet L. et al.. Transcript levels of AtMRPs after cadmium treatments, induction of AtMRP3. Plant Cell Environ. 26, 371–381 (2003).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

