Proteomic Analysis of Non-depleted Serum Proteins from Bottlenose Dolphins Uncovers a High Vanin-1 Phenotype
- PMID: 27667588
- PMCID: PMC5036180
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33879
Proteomic Analysis of Non-depleted Serum Proteins from Bottlenose Dolphins Uncovers a High Vanin-1 Phenotype
Abstract
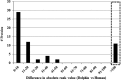
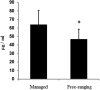
Targeted approaches have been widely used to help explain physiological adaptations, but few studies have used non-targeted omics approaches to explore differences between diving marine mammals and terrestrial mammals. A rank comparison of undepleted serum proteins from common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and pooled normal human serum led to the discovery of 11 proteins that appeared exclusive to dolphin serum. Compared to the comprehensive human plasma proteome, 5 of 11 serum proteins had a differential rank greater than 200. One of these proteins, Vanin-1, was quantified using parallel reaction monitoring in dolphins under human care and free-ranging dolphins. Dolphin serum Vanin-1 ranged between 31-106 μg/ml, which is 20-1000 times higher than concentrations reported for healthy humans. Serum Vanin-1 was also higher in dolphins under human care compared to free-ranging dolphins (64 ± 16 vs. 47 ± 12 μg/ml P < 0.05). Vanin-1 levels positively correlated with liver enzymes AST and ALT, and negatively correlated with white blood cell counts and fibrinogen in free-ranging dolphins. Major differences exist in the circulating blood proteome of the bottlenose dolphin compared to terrestrial mammals and exploration of these differences in bottlenose dolphins and other marine mammals may identify veiled protective strategies to counter physiological stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin blood concentration and vitamin supplementation in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in European facilities.BMC Vet Res. 2016 Sep 5;12(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0818-1. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27596136 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation and toxicological inference of trace elements in tissues from stranded and free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus).Chemosphere. 2011 Mar;82(11):1649-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.019. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Chemosphere. 2011. PMID: 21126751
-
Baseline circulating immunoglobulin G levels in managed collection and free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus).Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Apr;33(4):449-55. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.09.002. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18835295
-
Health Assessments of Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus): Past, Present, and Potential Conservation Applications.Front Vet Sci. 2019 Dec 13;6:444. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00444. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31921905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mini review of dolphin carbohydrate metabolism and suggestions for future research using exhaled air.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Dec 16;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00152. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 24379802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics reveals the preliminary physiological states of the spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 30;10(1):18727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75759-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33127980 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic screening of plasma identifies potential noninvasive biomarkers associated with significant/advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20190395. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190395. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31860081 Free PMC article.
-
Ice-Binding Proteins Associated with an Antarctic Cyanobacterium, Nostoc sp. HG1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jan 4;87(2):e02499-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02499-20. Print 2021 Jan 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33158891 Free PMC article.
-
Impact Effect of Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether "Twelve Months Vapor Inhalation Study in Rats".Biology (Basel). 2019 Dec 20;9(1):2. doi: 10.3390/biology9010002. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31861902 Free PMC article.
-
New de novo assembly of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) improves genome completeness and provides haplotype phasing.Gigascience. 2019 Mar 1;8(3):giy168. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy168. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 30698692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stenvinkel P. & Johnson R. J. Kidney biomimicry–a rediscovered scientific field that could provide hope to patients with kidney disease. Arch Med Res 44, 584–590 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Costa D. P. & Ortiz C. L. Blood chemistry homeostasis during prolonged fasting in the northern elephant seal. Am J Physiol 242, R591–R595 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Ridgway S. & Venn-Watson S. Effects of fresh and seawater ingestion on osmoregulation in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J Comp Physiol B 180, 563–576 (2010). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

