Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages
- PMID: 27667687
- PMCID: PMC5863951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.064
Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages
Abstract
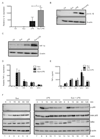
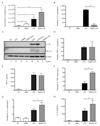
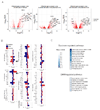
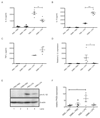
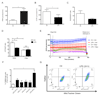
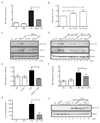
Activated macrophages undergo metabolic reprogramming, which drives their pro-inflammatory phenotype, but the mechanistic basis for this remains obscure. Here, we demonstrate that upon lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, macrophages shift from producing ATP by oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis while also increasing succinate levels. We show that increased mitochondrial oxidation of succinate via succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and an elevation of mitochondrial membrane potential combine to drive mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. RNA sequencing reveals that this combination induces a pro-inflammatory gene expression profile, while an inhibitor of succinate oxidation, dimethyl malonate (DMM), promotes an anti-inflammatory outcome. Blocking ROS production with rotenone by uncoupling mitochondria or by expressing the alternative oxidase (AOX) inhibits this inflammatory phenotype, with AOX protecting mice from LPS lethality. The metabolic alterations that occur upon activation of macrophages therefore repurpose mitochondria from ATP synthesis to ROS production in order to promote a pro-inflammatory state.
Keywords: immunometabolism; innate immunity; macrophage; reverse electron transport; succinate; succinate dehydrogenase; toll-like receptors.
Crown Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. MPM and CF have a patent application on the therapeutic application of SDH inhibitors.
Figures





References
-
- Barrientos A, Moraes CT. Titrating the effects of mitochondrial complex I impairment in the cell physiology. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:16188–16197. - PubMed
-
- Cassatella MA, Meda L, Gasperini S, Calzetti F, Bonora S. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) upregulates IL-1 receptor antagonist production from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by delaying mRNA degradation. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1994;179:1695–1699. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chance B, Hollunger G. The interaction of energy and electron transfer reactions in mitochondria. I. General properties and nature of the products of succinate-linked reduction of pyridine nucleotide. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1961;236:1534–1543. - PubMed
-
- Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE, Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM, Schumacker PT. Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25130–25138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

