A suppressor locus for MODY3-diabetes
- PMID: 27667715
- PMCID: PMC5036084
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33087
A suppressor locus for MODY3-diabetes
Erratum in
-
Erratum: A suppressor locus for MODY3-diabetes.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 21;6:35697. doi: 10.1038/srep35697. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27767025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
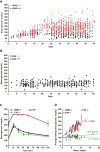
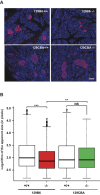
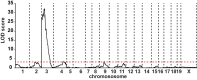
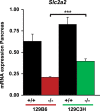
Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young type 3 (MODY3), linked to mutations in the transcription factor HNF1A, is the most prevalent form of monogenic diabetes mellitus. HNF1alpha-deficiency leads to defective insulin secretion via a molecular mechanism that is still not completely understood. Moreover, in MODY3 patients the severity of insulin secretion can be extremely variable even in the same kindred, indicating that modifier genes may control the onset of the disease. With the use of a mouse model for HNF1alpha-deficiency, we show here that specific genetic backgrounds (C3H and CBA) carry a powerful genetic suppressor of diabetes. A genome scan analysis led to the identification of a major suppressor locus on chromosome 3 (Moda1). Moda1 locus contains 11 genes with non-synonymous SNPs that significantly interacts with other loci on chromosomes 4, 11 and 18. Mechanistically, the absence of HNF1alpha in diabetic-prone (sensitive) strains leads to postnatal defective islets growth that is remarkably restored in resistant strains. Our findings are relevant to human genetics since Moda1 is syntenic with a human locus identified by genome wide association studies of fasting glycemia in patients. Most importantly, our results show that a single genetic locus can completely suppress diabetes in Hnf1a-deficiency.
Figures




References
-
- Kim S. H. et al.. Genetic modifiers of the age at diagnosis of diabetes (MODY3) in carriers of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha mutations map to chromosomes 5p15, 9q22, and 14q24. Diabetes 52, 2182–2186 (2003). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

