LongISLND: in silico sequencing of lengthy and noisy datatypes
- PMID: 27667791
- PMCID: PMC5167071
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw602
LongISLND: in silico sequencing of lengthy and noisy datatypes
Abstract
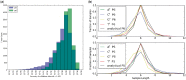
LongISLND is a software package designed to simulate sequencing data according to the characteristics of third generation, single-molecule sequencing technologies. The general software architecture is easily extendable, as demonstrated by the emulation of Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) multi-pass sequencing with P5 and P6 chemistries, producing data in FASTQ, H5, and the latest PacBio BAM format. We demonstrate its utility by downstream processing with consensus building and variant calling.
Availability and implementation: LongISLND is implemented in Java and available at http://bioinform.github.io/longislnd CONTACT: hugo.lam@roche.comSupplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Berlin K. et al. (2015) Assembling large genomes with single-molecule sequencing and locality-sensitive hashing. Nat. Biotechnol., 33, 623–630. - PubMed
-
- Chin C.S. et al. (2013) Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat. Methods, 10, 563–569. - PubMed
-
- Eid J. et al. (2009) Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science, 323, 133–138. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

