A three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with a palatal plate, pendulum, and headgear according to molar eruption stage
- PMID: 27668192
- PMCID: PMC5033768
- DOI: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.5.290
A three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with a palatal plate, pendulum, and headgear according to molar eruption stage
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to (1) evaluate the effects of maxillary second and third molar eruption status on the distalization of first molars with a modified palatal anchorage plate (MPAP), and (2) compare the results to the outcomes of the use of a pendulum and that of a headgear using three-dimensional finite element analysis.
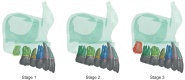
Methods: Three eruption stages were established: an erupting second molar at the cervical one-third of the first molar root (Stage 1), a fully erupted second molar (Stage 2), and an erupting third molar at the cervical one-third of the second molar root (Stage 3). Retraction forces were applied via three anchorage appliance models: an MPAP with bracket and archwire, a bone-anchored pendulum appliance, and cervical-pull headgear.
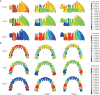
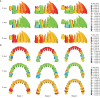
Results: An MPAP showed greater root movement of the first molar than crown movement, and this was more noticeable in Stages 2 and 3. With the other devices, the first molar showed distal tipping. Transversely, the first molar had mesial-out rotation with headgear and mesial-in rotation with the other devices. Vertically, the first molar was intruded with an MPAP, and extruded with the other appliances.
Conclusions: The second molar eruption stage had an effect on molar distalization, but the third molar follicle had no effect. The application of an MPAP may be an effective treatment option for maxillary molar distalization.
Keywords: Class II; Distalizing; Headgear; Palatal plate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary, or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures




Comment in
-
Reader's Forum.Korean J Orthod. 2016 Nov;46(6):343-344. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.6.343. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Korean J Orthod. 2016. PMID: 27896207 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004 Jan;125(1):8-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.02.002. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. PMID: 14718874
-
Effect of Second and Third Molar Eruption Stages on First Molar and Maxillary Arch Distalization With Modified Palatal Anchorage Plate and Beneslider: A 3D Finite Element Analysis.Cureus. 2024 May 31;16(5):e61403. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61403. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38947589 Free PMC article.
-
A 3D finite element analysis of maxillary molar distalization using unilateral zygoma gear and asymmetric headgear.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2021 May;24(2):261-267. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12430. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2021. PMID: 33001566
-
Treatment effects of intraoral appliances with conventional anchorage designs for non-compliance maxillary molar distalization: a literature review.Eur J Orthod. 2008 Dec;30(6):558-71. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn047. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Eur J Orthod. 2008. PMID: 18820306 Review.
-
Efficiency of molar distalization associated with second and third molar eruption stage.Angle Orthod. 2013 Jul;83(4):735-42. doi: 10.2319/081612-658.1. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Angle Orthod. 2013. PMID: 23167519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Three-dimensional evaluation of maxillary dentoalveolar changes and airway space after distalization in adults.Angle Orthod. 2018 Mar;88(2):187-194. doi: 10.2319/121116-889.1. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Angle Orthod. 2018. PMID: 29337633 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of treatment effects between the modified C-palatal plate and cervical pull headgear for total arch distalization in adults.Korean J Orthod. 2017 Nov;47(6):375-383. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2017.47.6.375. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Korean J Orthod. 2017. PMID: 29090125 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical effects of Teuscher activator in hyperdivergent Class II malocclusion treatment: A finite element analysis.J Clin Exp Dent. 2021 Nov 1;13(11):e1124-e1130. doi: 10.4317/jced.58722. eCollection 2021 Nov. J Clin Exp Dent. 2021. PMID: 34824699 Free PMC article.
-
Finite element analysis of maxillary arch distalization using skeletal anchorage at three different application regions.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 5;15(1):24073. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10035-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40617956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of early and later timed cervical headgear treatment on the eruption timing and pattern of permanent upper canines and molars from 7 to 18 years of age: follow-up of a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthod. 2025 Jun 12;47(4):cjaf056. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaf056. Eur J Orthod. 2025. PMID: 40576200 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Gianelly AA. Distal movement of the maxillary molars. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998;114:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Kinzinger GS, Fritz UB, Sander FG, Diedrich PR. Efficiency of a pendulum appliance for molar distalization related to second and third molar eruption stage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004;125:8–23. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson I, Bondemark L. Intraoral maxillary molar distalization. Angle Orthod. 2006;76:923–929. - PubMed
-
- Egolf RJ, BeGole EA, Upshaw HS. Factors associated with orthodontic patient compliance with intraoral elastic and headgear wear. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1990;97:336–348. - PubMed
-
- Lima Filho RM, Lima AL, de Oliveira Ruellas AC. Longitudinal study of anteroposterior and vertical maxillary changes in skeletal class II patients treated with Kloehn cervical headgear. Angle Orthod. 2003;73:187–193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
