Gene expression elucidates functional impact of polygenic risk for schizophrenia
- PMID: 27668389
- PMCID: PMC5083142
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4399
Gene expression elucidates functional impact of polygenic risk for schizophrenia
Abstract
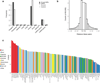
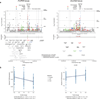
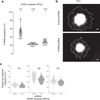
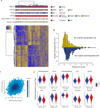
Over 100 genetic loci harbor schizophrenia-associated variants, yet how these variants confer liability is uncertain. The CommonMind Consortium sequenced RNA from dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of people with schizophrenia (N = 258) and control subjects (N = 279), creating a resource of gene expression and its genetic regulation. Using this resource, ∼20% of schizophrenia loci have variants that could contribute to altered gene expression and liability. In five loci, only a single gene was involved: FURIN, TSNARE1, CNTN4, CLCN3 or SNAP91. Altering expression of FURIN, TSNARE1 or CNTN4 changed neurodevelopment in zebrafish; knockdown of FURIN in human neural progenitor cells yielded abnormal migration. Of 693 genes showing significant case-versus-control differential expression, their fold changes were ≤ 1.33, and an independent cohort yielded similar results. Gene co-expression implicates a network relevant for schizophrenia. Our findings show that schizophrenia is polygenic and highlight the utility of this resource for mechanistic interpretations of genetic liability for brain diseases.
Figures


Comment in
-
Brains, genes and power.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Oct 26;19(11):1428-1430. doi: 10.1038/nn.4424. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27786186 No abstract available.
References
METHODS-ONLY REFERENCES
-
- Powchik P, et al. Postmortem studies in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998;24:325–341. - PubMed
-
- Purohit DP, et al. Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative diseases in elderly patients with schizophrenia: a postmortem neuropathologic study of 100 cases. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Glantz LA, Lewis DA. Decreased dendritic spine density on prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:65–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 MH094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH096891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH095034/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074313/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH087004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110555/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050986/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008451/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109677/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101454/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002395/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH105881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH096296/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

