Analysis of allelic expression patterns in clonal somatic cells by single-cell RNA-seq
- PMID: 27668657
- PMCID: PMC5117254
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3678
Analysis of allelic expression patterns in clonal somatic cells by single-cell RNA-seq
Abstract
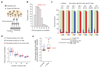
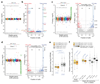
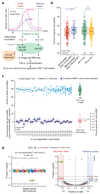
Cellular heterogeneity can emerge from the expression of only one parental allele. However, it has remained controversial whether, or to what degree, random monoallelic expression of autosomal genes (aRME) is mitotically inherited (clonal) or stochastic (dynamic) in somatic cells, particularly in vivo. Here we used allele-sensitive single-cell RNA-seq on clonal primary mouse fibroblasts and freshly isolated human CD8+ T cells to dissect clonal and dynamic monoallelic expression patterns. Dynamic aRME affected a considerable portion of the cells' transcriptomes, with levels dependent on the cells' transcriptional activity. Notably, clonal aRME was detected, but it was surprisingly scarce (<1% of genes) and mainly affected the most weakly expressed genes. Consequently, the overwhelming majority of aRME occurs transiently within individual cells, and patterns of aRME are thus primarily scattered throughout somatic cell populations rather than, as previously hypothesized, confined to patches of clonally related cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
High prevalence of clonal monoallelic expression.Nat Genet. 2018 Sep;50(9):1198-1199. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0188-7. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 30082785 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

