Evaluation of a novel autoinjector for subcutaneous self-administration of belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 27668697
- PMCID: PMC5100660
- DOI: 10.5414/CP202623
Evaluation of a novel autoinjector for subcutaneous self-administration of belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: To study self-administration and pharmacokinetics (PK) of subcutaneous (SC) belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
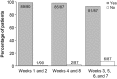
Methods: Patients previously treated with belimumab self-administered belimumab 200 mg SC weekly for 8 weeks using an autoinjector. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients able to self-administer their first and second dose (weeks 1 and 2) in the clinic. The proportion able to self-administer at weeks 4 and 8 (clinic) and weeks 3, 5, 6, and 7 (home) were secondary endpoints. Belimumab PK, safety, and injection-site pain were assessed.
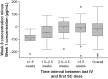
Results: 91/95 patients completed the study (withdrawals: adverse events (AEs): 3; lost to follow-up: 1). 93% were female, and mean (SD) age was 44.8 (12.50) years. The majority (99%, 89/90; no attempt, n = 5) successfully self-administered belimumab SC at weeks 1 and 2 (5 had clinic staff assistance), and 98% (85/87) successfully self-administered at weeks 4 and 8. Home-administration success rates were high (93%, (81/87) at weeks 3, 5, 6, and 7). Week 8 median trough concentration was 113 µg/mL. For patients with a ≤ 1.5-week interval between IV SC administration, week-1 concentrations were higher vs. week 8 (+ 51% median) but within a range observed with IV dosing; those with a ≥ 2.5-week interval had median differences close to 0. AEs and serious AEs were low, with no deaths; pain levels were low and decreased with subsequent injections.
Conclusion: Patients with SLE successfully self-administered belimumab SC using a novel autoinjector; the PK profile was stable following a switch from IV with acceptable AE and pain levels. The recommended dosing interval between IV to SC dosing is 1 - 4 weeks. .
Figures




References
-
- Lau CS Mak A The socioeconomic burden of SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5: 400–404. - PubMed
-
- Baker KP Edwards BM Main SH Choi GH Wager RE Halpern WG Lappin PB Riccobene T Abramian D Sekut L Sturm B Poortman C Minter RR Dobson CL Williams E Carmen S Smith R Roschke V Hilbert DM Vaughan TJ Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48: 3253–3265. - PubMed
-
- Furie R Petri M Zamani O Cervera R Wallace DJ Tegzová D Sanchez-Guerrero J Schwarting A Merrill JT Chatham WW Stohl W Ginzler EM Hough DR Zhong ZJ Freimuth W van Vollenhoven RF A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63: 3918–3930. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Navarra SV Guzmán RM Gallacher AE Hall S Levy RA Jimenez RE Li EK Thomas M Kim HY León MG Tanasescu C Nasonov E Lan JL Pineda L Zhong ZJ Freimuth W Petri MA Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011; 377: 721–731. - PubMed
-
- GlaxoSmithKline. Benlysta (belimumab) Prescribing Information. 2014. p. 1-24. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/125370s016lbl.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

