Bacterial fatty acid metabolism in modern antibiotic discovery
- PMID: 27668701
- PMCID: PMC5364071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.014
Bacterial fatty acid metabolism in modern antibiotic discovery
Abstract
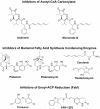
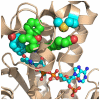
Bacterial fatty acid synthesis is essential for many pathogens and different from the mammalian counterpart. These features make bacterial fatty acid synthesis a desirable target for antibiotic discovery. The structural divergence of the conserved enzymes and the presence of different isozymes catalyzing the same reactions in the pathway make bacterial fatty acid synthesis a narrow spectrum target rather than the traditional broad spectrum target. Furthermore, bacterial fatty acid synthesis inhibitors are single-targeting, rather than multi-targeting like traditional monotherapeutic, broad-spectrum antibiotics. The single-targeting nature of bacterial fatty acid synthesis inhibitors makes overcoming fast-developing, target-based resistance a necessary consideration for antibiotic development. Target-based resistance can be overcome through multi-targeting inhibitors, a cocktail of single-targeting inhibitors, or by making the single targeting inhibitor sufficiently high affinity through a pathogen selective approach such that target-based mutants are still susceptible to therapeutic concentrations of drug. Many of the pathogens requiring new antibiotic treatment options encode for essential bacterial fatty acid synthesis enzymes. This review will evaluate the most promising targets in bacterial fatty acid metabolism for antibiotic therapeutics development and review the potential and challenges in advancing each of these targets to the clinic and circumventing target-based resistance. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Bacterial Lipids edited by Russell E. Bishop.
Keywords: Antibiotic discovery; Bacterial fatty acid synthesis; Resistance.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure, inhibition, and regulation of essential lipid A enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Nov;1862(11):1424-1438. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 27940308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Bacterial Transglycosylase: Antibiotic Development from a Structural Perspective.ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 13;5(9):1493-1504. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00118. Epub 2019 Jul 8. ACS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31283163 Review.
-
Inhibitors of FabI, an enzyme drug target in the bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis pathway.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Jan;41(1):11-20. doi: 10.1021/ar700156e. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 18193820 Review.
-
Molecules that Inhibit Bacterial Resistance Enzymes.Molecules. 2018 Dec 22;24(1):43. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010043. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30583527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis: targets for antibacterial drug discovery.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:305-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.305. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11544358
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Stilbenes from Bletilla striata against Cutibacterium acnes and Its Effect on Cell Membrane.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 11;11(12):2958. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11122958. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38138103 Free PMC article.
-
Overview on Strategies and Assays for Antibiotic Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;15(10):1302. doi: 10.3390/ph15101302. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targets in Chlamydial Fatty Acid and Phospholipid Synthesis.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 25;9:2291. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02291. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30319589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the chemical space of 1,2,3-triazolyl triclosan analogs for discovery of new antileishmanial chemotherapeutic agents.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Nov 5;12(1):120-128. doi: 10.1039/d0md00291g. eCollection 2021 Jan 1. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046604 Free PMC article.
-
An Iterative Approach Guides Discovery of the FabI Inhibitor Fabimycin, a Late-Stage Antibiotic Candidate with In Vivo Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections.ACS Cent Sci. 2022 Aug 24;8(8):1145-1158. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c00598. Epub 2022 Aug 10. ACS Cent Sci. 2022. PMID: 36032774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strebhardt K, Ullrich A. Paul Ehrlich's magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:473–480. - PubMed
-
- Lesch JE. Prontosil, The first miracle drugs: how the sulfa drugs transformed medicine. Oxford University Press; 2006. p. 51.
-
- Brown ED, Wright GD. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature (London) 2016;529:336–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

