RESPONSIVENESS OF THE NATIONAL EYE INSTITUTE VISUAL FUNCTION QUESTIONNAIRE-25 TO VISUAL ACUITY GAINS IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA: Evidence From the RIDE and RISE Trials
- PMID: 27668928
- PMCID: PMC5470864
- DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001316
RESPONSIVENESS OF THE NATIONAL EYE INSTITUTE VISUAL FUNCTION QUESTIONNAIRE-25 TO VISUAL ACUITY GAINS IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA: Evidence From the RIDE and RISE Trials
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the responsiveness of the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire-25 (NEI VFQ-25) in patients with diabetic macular edema using data from the RIDE and RISE trials.
Methods: Patients were randomized to monthly intravitreal ranibizumab 0.3 mg, 0.5 mg, or sham injections for 2 years. The NEI VFQ-25 was administered at baseline and at Months 6, 12, 18, and 24. The least-squares mean change in NEI VFQ-25 for ≥15 letters gained or lost was derived from analysis of covariance models.
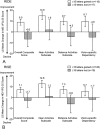
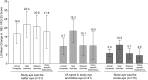
Results: The mean improvement in NEI VFQ-25 composite score associated with a ≥15-letter gain in best-corrected visual acuity over 24 months was 9.0 (95% confidence interval, 6.3-11.7) points in RIDE and 7.1 (95% confidence interval, 4.7-9.6) points in RISE. In patients who lost ≥15 letters, the mean worsening in overall NEI VFQ-25 composite score was -6.6 (95% confidence interval, -13.6 to 0.5) in RIDE and -2.7 (95% confidence interval, -8.9 to 3.5) in RISE.
Conclusion: This exploratory analysis of data from the RIDE and RISE studies supports the responsiveness of the NEI VFQ-25 to changes in best-corrected visual acuity over time in patients with diabetic macular edema.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vision-related function after ranibizumab treatment for diabetic macular edema: results from RIDE and RISE.Ophthalmology. 2014 Dec;121(12):2461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Ophthalmology. 2014. PMID: 25148789 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Ranibizumab on the Decision to Drive and Vision Function Relevant to Driving in Patients With Diabetic Macular Edema: Report From RESTORE, RIDE, and RISE Trials.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016 Feb;134(2):160-6. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.4636. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26584450 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinically Meaningful Change Estimates for the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire-25 in Patients With Diabetic Macular Edema.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Dec 2;13(12):27. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.12.27. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39680390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[New perspectives in the approach to diabetic macular edema. Aflibercept therapy].Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015 Mar;90 Suppl 1:24-8. doi: 10.1016/S0365-6691(15)30006-X. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 25925048 Review. Spanish.
-
Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Diabetic Macular Edema: Long-Term Outcomes.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;60:63-70. doi: 10.1159/000460496. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28427066 Review.
Cited by
-
The negative effects of dry eye disease on quality of life and visual function.Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Nov 3;50(SI-2):1611-1615. doi: 10.3906/sag-2002-143. Turk J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32283910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of fluocinolone acetonide 0.2 μg/day implant on the decision to drive in patients with diabetic macular oedema: a report from the FAME study.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2019 Dec 15;4(1):e000405. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2019-000405. eCollection 2019. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31909197 Free PMC article.
-
Near vision in patients with DME and RVO treated with aflibercept and correlation with NEI VFQ-25 questionnaire.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024 May 23;10(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40942-024-00558-0. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024. PMID: 38783380 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-reported outcomes from a phase IV study of aflibercept in patients with refractory retinal vein occlusions.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jun 3;11(3):244-250. doi: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_19_20. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 34703739 Free PMC article.
-
Burden Of Treatment Among Patients Undergoing Intravitreal Injections For Diabetic Macular Oedema In Australia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Sep 19;12:1913-1921. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S214098. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31571965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Fact Sheet: National Estimates and General Information on Diabetes and Prediabetes in the United States. 2011. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf. Accessed December 12, 2013.
-
- Lamoureux EL, Tai ES, Thumboo J, et al. Impact of diabetic retinopathy on vision-specific function. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:757–765. - PubMed
-
- Trento M, Passera P, Trevisan M, et al. Quality of life, impaired vision and social role in people with diabetes: a multicenter observational study. Acta Diabetol. 2013;50:873–877. - PubMed
-
- Ciulla TA, Amador AG, Zinman B. Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2653–2664. - PubMed
-
- Hariprasad SM, Mieler WF, Grassi M, et al. Vision-related quality of life in patients with diabetic macular oedema. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92:89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

