E4 ligase-specific ubiquitination hubs coordinate DNA double-strand-break repair and apoptosis
- PMID: 27669035
- PMCID: PMC5349472
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3296
E4 ligase-specific ubiquitination hubs coordinate DNA double-strand-break repair and apoptosis
Abstract
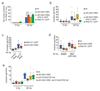
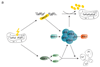
Multiple protein ubiquitination events at DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) regulate damage recognition, signaling and repair. It has remained poorly understood how the repair process of DSBs is coordinated with the apoptotic response. Here, we identified the E4 ubiquitin ligase UFD-2 as a mediator of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis in a genetic screen in Caenorhabditis elegans. We found that, after initiation of homologous recombination by RAD-51, UFD-2 forms foci that contain substrate-processivity factors including the ubiquitin-selective segregase CDC-48 (p97), the deubiquitination enzyme ATX-3 (Ataxin-3) and the proteasome. In the absence of UFD-2, RAD-51 foci persist, and DNA damage-induced apoptosis is prevented. In contrast, UFD-2 foci are retained until recombination intermediates are removed by the Holliday-junction-processing enzymes GEN-1, MUS-81 or XPF-1. Formation of UFD-2 foci also requires proapoptotic CEP-1 (p53) signaling. Our findings establish a central role of UFD-2 in the coordination between the DNA-repair process and the apoptotic response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

