Characterization of a β-Adrenergic-Like Octopamine Receptor in the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)
- PMID: 27669213
- PMCID: PMC5085626
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17101577
Characterization of a β-Adrenergic-Like Octopamine Receptor in the Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)
Abstract
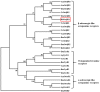
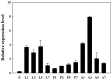
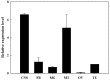
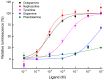
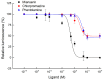
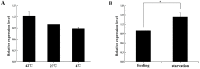
The biogenic amine octopamine plays a critical role in the regulation of many physiological processes in insects. Octopamine transmits its action through a set of specific G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), namely octopamine receptors. Here, we report on a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor gene (BdOctβR1) from the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel), a destructive agricultural pest that occurs in North America and the Asia-Pacific region. As indicated by RT-qPCR, BdOctβR1 was highly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) and Malpighian tubules (MT) in the adult flies, suggesting it may undertake important roles in neural signaling in the CNS as well as physiological functions in the MT of this fly. Furthermore, its ligand specificities were tested in a heterologous expression system where BdOctβR1 was expressed in HEK-293 cells. Based on cyclic AMP response assays, we found that BdOctβR1 could be activated by octopamine in a concentration-dependent manner, confirming that this receptor was functional, while tyramine and dopamine had much less potency than octopamine. Naphazoline possessed the highest agonistic activity among the tested agonists. In antagonistic assays, mianserin had the strongest activity and was followed by phentolamine and chlorpromazine. Furthermore, when the flies were kept under starvation, there was a corresponding increase in the transcript level of BdOctβR1, while high or low temperature stress could not induce significant expression changes. The above results suggest that BdOctβR1 may be involved in the regulation of feeding processes in Bactrocera dorsalis and may provide new potential insecticide leads targeting octopamine receptors.
Keywords: Bactrocera dorsalis; agonist; antagonist; biogenic amine; cyclic AMP; functional expression; octopamine receptor; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor from the rice stem borer (Chilo suppressalis).J Exp Biol. 2012 Aug 1;215(Pt 15):2646-52. doi: 10.1242/jeb.068932. J Exp Biol. 2012. PMID: 22786641
-
Pharmacological characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in Plutella xylostella.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2018 Aug;98(4):e21466. doi: 10.1002/arch.21466. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29691888
-
Pharmacological characterisation and functional roles for egg-laying of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Aug;87:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28629966
-
Insect octopamine receptors: a new classification scheme based on studies of cloned Drosophila G-protein coupled receptors.Invert Neurosci. 2005 Nov;5(3-4):111-8. doi: 10.1007/s10158-005-0001-z. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Invert Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16211376 Review.
-
Tyramine: from octopamine precursor to neuroactive chemical in insects.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009 May 15;162(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.05.021. Epub 2008 Jun 8. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 18588893 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Insecticidal Activity of Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids from Chilean Rhamnaceae Plants against Fruit-Fly Drosophila melanogaster and the Lepidopteran Crop Pest Cydia pomonella.Molecules. 2020 Nov 3;25(21):5094. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215094. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33153001 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Biogenic Amines in Oviposition by the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella L.Front Physiol. 2020 May 18;11:475. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00475. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32528307 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Pharmacological Characterization of β-Adrenergic-like Octopamine Receptors in the Endoparasitoid Cotesia chilonis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 22;23(23):14513. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314513. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498840 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of a β-Adrenergic-Like Octopamine Receptor Affects Locomotion and Reproduction of Tribolium castaneum.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7252. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147252. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298876 Free PMC article.
-
She's got nerve: roles of octopamine in insect female reproduction.J Neurogenet. 2021 Sep;35(3):132-153. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1868457. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Neurogenet. 2021. PMID: 33909537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

