Effect of Vitamin A on Listeria monocytogenes Infection in a Silkworm Model
- PMID: 27669511
- PMCID: PMC5036829
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163747
Effect of Vitamin A on Listeria monocytogenes Infection in a Silkworm Model
Abstract
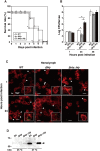
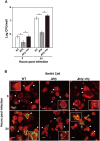
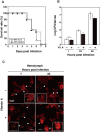
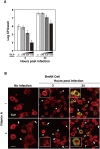
Insect infection models have been used increasingly to study various pathogenic agents in evaluations of pathogenicity and drug efficacy. In this study, we demonstrated that larvae of the silkworm Bombyx mori are useful for studying Listeria monocytogenes infections in insects. Infection with the L. monocytogenes wild-type strain induced silkworm death. Infection by a listeriolysin O (LLO) deletion mutant also induced silkworm death, but the bacterial numbers in silkworms were lower than those of the wild-type strain. Intracellular growth was observed when the silkworm ovary-derived cell line BmN4 was infected with the wild-type strain. Explosive replication was not observed in BmN4 cells infected with the LLO mutant and the bacterial numbers of the LLO mutant were lower than those of the wild-type strain. Pretreatment with vitamin A did not affect silkworm mortality after bacterial infection, but the efficiency of infecting the hemocytes and BmN4 cells was decreased with vitamin A treatment. Our results indicate that silkworm larvae are a useful insect infection model for L. monocytogenes and that vitamin A has protective effects against bacterial infection in silkworms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silkworm model for Francisella novicida infection.Microb Pathog. 2017 Dec;113:94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.10.036. Epub 2017 Oct 21. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29066381
-
Curcumin Promotes the Clearance of Listeria monocytogenes both In Vitro and In Vivo by Reducing Listeriolysin O Oligomers.Front Immunol. 2017 May 17;8:574. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00574. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28567044 Free PMC article.
-
Cytolysin-dependent escape of the bacterium from the phagosome is required but not sufficient for induction of the Th1 immune response against Listeria monocytogenes infection: distinct role of Listeriolysin O determined by cytolysin gene replacement.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):3791-801. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01779-06. Epub 2007 May 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17517863 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism and potential application of bacterial infection in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.Dev Comp Immunol. 2022 Jun;131:104381. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2022.104381. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35245606 Review.
-
[Identification of novel therapeutically effective antibiotics using silkworm infection model].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(1):79-84. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.132.79. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22214583 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A novel silkworm infection model with fluorescence imaging using transgenic Trichosporon asahii expressing eGFP.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 3;10(1):10991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67841-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32620930 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of colon-targeted vitamins on the composition and metabolic activity of the human gut microbiome- a pilot study.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1-20. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1875774. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 33615992 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Silkworm model of bacterial infection facilitates the identification of lysocin E, a potent, ultra-rapid bactericidal antibiotic.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024 Aug;77(8):477-485. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00739-x. Epub 2024 May 21. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38773231 Review.
-
Advances in Editing Silkworms (Bombyx mori) Genome by Using the CRISPR-Cas System.Insects. 2021 Dec 27;13(1):28. doi: 10.3390/insects13010028. Insects. 2021. PMID: 35055871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of food-derived bioactives on gut microbiota compositions and their metabolites by focusing on neurotransmitters.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 30;32(8):1019-1027. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01293-2. eCollection 2023 Jul. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37215258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

