Preloading of Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug into Multifunctional Nanocarrier for Multimodal Imaging, NIR-Responsive Drug Release, and Synergistic Therapy
- PMID: 27671114
- PMCID: PMC5253133
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.201602263
Preloading of Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug into Multifunctional Nanocarrier for Multimodal Imaging, NIR-Responsive Drug Release, and Synergistic Therapy
Abstract
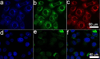
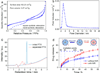
Applications of hydrophobic drug-based nanocarriers (NCs) remain largely limited because of their low loading capacity. Here, development of a multifunctional hybrid NC made of a magnetic Fe3O4 core and a mesoporous silica shell embedded with carbon dots (CDs) and paclitaxel (PTX), and covered by another layer of silica is reported. The NC is prepared via a one-pot process under mild condition. The PTX loading method introduced in this study simplifies drug loading process and demonstrates a high loading capacity due to mesoporous silica dual-shell structure, supramolecular π-stacking between conjugated rings of PTX molecules, and aromatic rings of the CDs in the hybrid NC. The CDs serve as both confocal and two-photon fluorescence imaging probes, while the Fe3O4 core serves as a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Significantly, NC releases PTX in response to near infrared irradiation as a result of local heating of the embedded CDs and the heating of CDs also provides an additional therapeutic effect by thermally killing cancer cells in tumor in addition to the chemotherapeutic effect of released PTX. Both in vitro and in vivo results show that NC demonstrates high therapeutic efficacy through a synergistic effect from the combined chemo-photothermal treatments.
Keywords: hydrophobic drugs; mesoporous silica; multifunctional imaging; preloading; synergistic effects.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



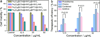

References
-
- Chabner BA, Roberts TG. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5(1):65–72. - PubMed
-
- Lipinski CA. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2000;44(1):235–249. DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1056-8719(00)00107-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Merisko-Liversidge EM, Liversidge GG. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008;36(1):43–48. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Liong M, Zink JI, Tamanoi F. Small. 2007;3(8):1341–1346. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Yan Y, Cui J, Hosta-Rigau L, Heath JK, Nice EC, Caruso F. Adv. Mater. 2010;22(38):4293–4297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

