Arid5a exacerbates IFN-γ-mediated septic shock by stabilizing T-bet mRNA
- PMID: 27671645
- PMCID: PMC5068254
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1613307113
Arid5a exacerbates IFN-γ-mediated septic shock by stabilizing T-bet mRNA
Abstract
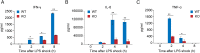
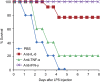
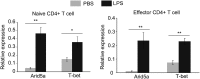
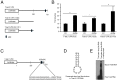
Adenine-thymine (AT)-rich interactive domain containing protein 5a (Arid5a) is an RNA-binding protein that has been shown to play an important immune regulatory function via the stabilization of IL-6 and STAT3 mRNA. However, the role of Arid5a in the overwhelming and uncontrolled immune response that leads to septic shock is unknown. Here, we report that Arid5a-deficient mice are highly resistant to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock and secrete lower levels of major proinflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-6, and TNF-α, than WT mice in response to LPS. Arid5a deficiency resulted in decreased levels of IFN-γ under Th1 cell conditions, in which T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet) mRNA expression was inhibited. Arid5a bound to the conserved stem loop structure of the 3'UTR of T-bet and stabilized its mRNA. Arid5a-deficient mice were also resistant to Propionibacterium acnes-primed LPS injection, which is considered to be a T-cell-mediated IFN-γ dependent endotoxic shock mouse model. Thus, regulation of IFN-γ by Arid5a via the stabilization of T-bet mRNA in Th1 cells contributes to the development of septic shock in mice. In addition, our previous study suggests that Arid5a control the IL-6 level in vivo in response to LPS by stabilization of IL-6 mRNA. We also observed that neutralization of IFN-γ and IL-6 significantly recovered the mice from endotoxic shock. Taken together, we conclude that Arid5a regulates the augmentation of IL-6 and IFN-γ in response to LPS, which possibly works synergistically for amplification of various other cytokines that ultimately cause the development of septic shock in mice.
Keywords: Arid5a; IFN-γ; IL-6; T-bet; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Comment in
-
Sepsis: Therapeutic Potential of Immunosuppression versus Immunostimulation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Jan;60(1):128-130. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0284RO. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30230345 No abstract available.
References
-
- Farrar MA, Schreiber RD. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11(1):571–611. - PubMed
-
- Heinzel FP. The role of IFN-gamma in the pathology of experimental endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1990;145(9):2920–2924. - PubMed
-
- Enoh VT, et al. Mice depleted of alphabeta but not gammadelta T cells are resistant to mortality caused by cecal ligation and puncture. Shock. 2007;27(5):507–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

