Phosphatidic acid and neurotransmission
- PMID: 27671966
- PMCID: PMC5292084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.09.004
Phosphatidic acid and neurotransmission
Abstract
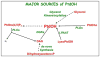
Lipids play a vital role in the health and functioning of neurons and interest in the physiological role of neuronal lipids is certainly increasing. One neuronal function in which neuronal lipids appears to play key roles in neurotransmission. Our understanding of the role of lipids in the synaptic vesicle cycle and neurotransmitter release is becoming increasingly more important. Much of the initial research in this area has highlighted the major roles played by the phosphoinositides (PtdIns), diacylglycerol (DAG), and phosphatidic acid (PtdOH). Of these, PtdOH has not received as much attention as the other lipids although its role and metabolism appears to be extremely important. This lipid has been shown to play a role in modulating both exocytosis and endocytosis although its precise role in either process is not well defined. The currently evidence suggest this lipid likely participates in key processes by altering membrane architecture necessary for membrane fusion, mediating the penetration of membrane proteins, serving as a precursor for other important SV cycling lipids, or activating essential enzymes. In this review, we address the sources of PtdOH, the enzymes involved in its production, the regulation of these enzymes, and its potential roles in neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diacylglycerol, phosphatidic acid, and their metabolic enzymes in synaptic vesicle recycling.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:147-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidic acid-producing enzymes regulating the synaptic vesicle cycle: Role for PLD?Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Jan;67:141-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.09.009. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 28986032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Lipids in the process of synaptic vesicle exo- and endocytosis].Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2010 Aug;96(8):753-65. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2010. PMID: 20968061 Review. Russian.
-
Regulation and roles of neuronal diacylglycerol kinases: a lipid perspective.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Oct;46(5):353-64. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2011.577761. Epub 2011 May 4. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21539478 Review.
-
An overview of the synaptic vesicle lipid composition.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep 30;709:108966. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.108966. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34139199 Review.
Cited by
-
The hypothetical role of phosphatidic acid in subverting ER membranes during SARS-CoV infection.Traffic. 2020 Aug;21(8):545-551. doi: 10.1111/tra.12738. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Traffic. 2020. PMID: 32424954 Free PMC article.
-
SLC6 transporter oligomerization.J Neurochem. 2021 May;157(4):919-929. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15145. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 32767560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Phospholipase D from Moritella sp. JT01: Biochemical Characterization, Crystallization and Application in the Synthesis of Phosphatidic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 1;23(19):11633. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911633. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232934 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma membrane phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate promotes Weibel-Palade body exocytosis.Life Sci Alliance. 2020 Aug 21;3(11):e202000788. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000788. Print 2020 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2020. PMID: 32826291 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Synuclein and Lipids: The Elephant in the Room?Cells. 2021 Sep 17;10(9):2452. doi: 10.3390/cells10092452. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aalmo K, Hansen L, Hough E, Jynge K, Krane J, Little C, et al. An anion binding site in the active centre of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. BiochemInt. 1984;8:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Almena M, Merida I. Shaping up the membrane: diacylglycerol coordinates spatial orientation of signaling. Trends in biochemical sciences. 2011;36:593–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

