Crosstalk between androgen and pro-inflammatory signaling remodels androgen receptor and NF-κB cistrome to reprogram the prostate cancer cell transcriptome
- PMID: 27672034
- PMCID: PMC5314794
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw855
Crosstalk between androgen and pro-inflammatory signaling remodels androgen receptor and NF-κB cistrome to reprogram the prostate cancer cell transcriptome
Abstract
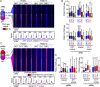
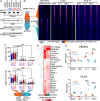
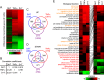
Inflammatory processes and androgen signaling are critical for the growth of prostate cancer (PC), the most common cancer among males in Western countries. To understand the importance of potential interplay between pro-inflammatory and androgen signaling for gene regulation, we have interrogated the crosstalk between androgen receptor (AR) and NF-κB, a key transcriptional mediator of inflammatory responses, by utilizing genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing and global run-on sequencing in PC cells. Co-stimulation of LNCaP cells with androgen and pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα invoked a transcriptome which was very distinct from that induced by either stimulation alone. The altered transcriptome that included gene programs linked to cell migration and invasiveness was orchestrated by significant remodeling of NF-κB and AR cistrome and enhancer landscape. Although androgen multiplied the NF-κB cistrome and TNFα restrained the AR cistrome, there was no general reciprocal tethering of the AR to the NF-κB on chromatin. Instead, redistribution of FOXA1, PIAS1 and PIAS2 contributed to the exposure of latent NF-κB chromatin-binding sites and masking of AR chromatin-binding sites. Taken together, concomitant androgen and pro-inflammatory signaling significantly remodels especially the NF-κB cistrome, reprogramming the PC cell transcriptome in fashion that may contribute to the progression of PC.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SUMO ligase PIAS1 functions as a target gene selective androgen receptor coregulator on prostate cancer cell chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(2):848-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1375. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25552417 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of nuclear factor-kappaB and B-myb in the negative regulation of androgen receptor expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Feb;22(2):273-86. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0332. Epub 2007 Nov 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 17975021 Free PMC article.
-
Darolutamide antagonizes androgen signaling by blocking enhancer and super-enhancer activation.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):2022-2039. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12693. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32333502 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor enhancer usage and the chromatin regulatory landscape in human prostate cancers.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019 May;26(5):R267-R285. doi: 10.1530/ERC-19-0032. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30865928 Review.
-
Chromatin binding by the androgen receptor in prostate cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Sep 5;360(1-2):44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.09.037. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21989426 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplex imaging of localized prostate tumors reveals altered spatial organization of AR-positive cells in the microenvironment.iScience. 2024 Aug 3;27(9):110668. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110668. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39246442 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-96 and RARγ signaling axis governs androgen signaling and prostate cancer progression.Oncogene. 2019 Jan;38(3):421-444. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0450-6. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30120411 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic nucleosome landscape elicits a noncanonical GATA2 pioneer model.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 7;13(1):3145. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30960-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35672415 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6 may influence ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration by regulating the NF-κB pathway.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):298-306. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10306. Epub 2019 May 3. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289500 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol A-induced DNA damages promote to lymphoma progression in human lymphoblastoid cells through aberrant CTNNB1 signaling pathway.iScience. 2021 Jul 21;24(8):102888. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102888. eCollection 2021 Aug 20. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34401669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vis A.N., Schroder F.H. Key targets of hormonal treatment of prostate cancer. part 2: the androgen receptor and 5alpha-reductase. BJU Int. 2009;104:1191–1197. - PubMed
-
- Shafi A.A., Yen A.E., Weigel N.L. Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013;140:223–238. - PubMed
-
- Mizokami A., Gotoh A., Yamada H., Keller E.T., Matsumoto T. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha represses androgen sensitivity in the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line. J. Urol. 2000;164:800–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

