Efficacy of Treatment of Non-hereditary Angioedema
- PMID: 27672078
- PMCID: PMC6002429
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-016-8585-0
Efficacy of Treatment of Non-hereditary Angioedema
Abstract
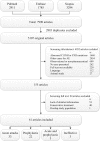
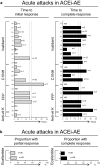
Non-hereditary angioedema (AE) with normal C1 esterase inhibitor (C1INH) can be presumably bradykinin- or mast cell-mediated, or of unknown cause. In this systematic review, we searched PubMed, EMBASE, and Scopus to provide an overview of the efficacy of different treatment options for the abovementioned subtypes of refractory non-hereditary AE with or without wheals and with normal C1INH. After study selection and risk of bias assessment, 61 articles were included for data extraction and analysis. Therapies were described for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced AE (ACEi-AE), for idiopathic AE, and for AE with wheals. Described treatments consisted of ecallantide, icatibant, C1INH, fresh frozen plasma (FFP), tranexamic acid (TA), and omalizumab. Additionally, individual studies for anti-vitamin K, progestin, and methotrexate were found. Safety information was available in 26 articles. Most therapies were used off-label and in few patients. There is a need for additional studies with a high level of evidence. In conclusion, in acute attacks of ACEi-AE and idiopathic AE, treatment with icatibant, C1INH, TA, and FFP often leads to symptom relief within 2 h, with limited side effects. For prophylactic treatment of idiopathic AE and AE with wheals, omalizumab, TA, and C1INH were effective and safe in the majority of patients.
Keywords: Angioedema; Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; Idiopathic; Treatment; Wheals.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
M.T. van den Elzen has received speaker’s fees from Novartis. A.C. Knulst is a member of the national and international Novartis Omalizumab Advisory Council and has received speaker’s fees from Novartis and sponsoring for scientific studies from Novartis and Pharming. The rest of the authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Funding
None.
Figures


References
-
- Lewis LM, Graffeo C, Crosley P, Klausner HA, Clark CL, Frank A, et al. Ecallantide for the acute treatment of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;65:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

