Natural Compounds as Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1 β Production
- PMID: 27672241
- PMCID: PMC5031844
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/5460302
Natural Compounds as Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1 β Production
Abstract
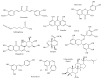
IL-1β is one of the main proinflammatory cytokines that regulates a broad range of immune responses and also participates in several physiological processes. The canonical production of IL-1β requires multiprotein complexes called inflammasomes. One of the most intensively studied inflammasome complexes is the NLRP3 inflammasome. Its activation requires two signals: one signal "primes" the cells and induces the expression of NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β, while the other signal leads to the assembly and activation of the complex. Several stimuli were reported to function as the second signal including reactive oxygen species, lysosomal rupture, or cytosolic ion perturbation. Despite very intensive studies, the precise function and regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome are still not clear. However, many chronic inflammatory diseases are related to the overproduction of IL-1β that is mediated via the NLRP3 inflammasome. In this review, we aimed to provide an overview of studies that demonstrated the effect of plant-derived natural compounds on NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated IL-1β production. Although many of these studies lack the mechanistic explanation of their action, these compounds may be considered as complementary supplements in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases, consumed as preventive agents, and may also be considered as molecular tools to study NLRP3 function.
Figures
References
-
- Romero L. I., Zhang D.-N., Herron G. S., Karasek M. A. Interleukin-1 induces major phenotypic changes in human skin microvascular endothelial cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1997;173(1):84–92. - PubMed
-
- Gabay E., Wolf G., Shavit Y., Yirmiya R., Tal M. Chronic blockade of interleukin-1 (IL-1) prevents and attenuates neuropathic pain behavior and spontaneous ectopic neuronal activity following nerve injury. European Journal of Pain. 2011;15(3):242–248. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.07.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources