Aberrant regulation of Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27672271
- PMCID: PMC5011664
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7486
Aberrant regulation of Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
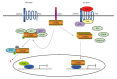
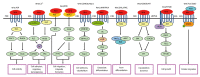
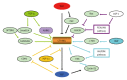
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal malignancies in the world. Several signaling pathways, including the wingless/int-1 (Wnt) signaling pathway, have been shown to be commonly activated in HCC. The Wnt signaling pathway can be triggered via both catenin β1 (CTNNB1)-dependent (also known as "canonical") and CTNNB1-independent (often referred to as "non-canonical") pathways. Specifically, the canonical Wnt pathway is one of those most frequently reported in HCC. Aberrant regulation from three complexes (the cell-surface receptor complex, the cytoplasmic destruction complex and the nuclear CTNNB1/T-cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer binding factor transcriptional complex) are all involved in HCC. Although the non-canonical Wnt pathway is rarely reported, two main non-canonical pathways, Wnt/planar cell polarity pathway and Wnt/Ca(2+) pathway, participate in the regulation of hepatocarcinogenesis. Interestingly, the canonical Wnt pathway is antagonized by non-canonical Wnt signaling in HCC. Moreover, other signaling cascades have also been demonstrated to regulate the Wnt pathway through crosstalk in HCC pathogenesis. This review provides a perspective on the emerging evidence that the aberrant regulation of Wnt signaling is a critical mechanism for the development of HCC. Furthermore, crosstalk between different signaling pathways might be conducive to the development of novel molecular targets of HCC.
Keywords: Canonical wingless/int-1 signaling; Catenin β1; Crosstalk; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Non-canonical wingless/int-1 signaling; Wingless/int-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Kawai-Kitahata F, Asahina Y, Tanaka S, Kakinuma S, Murakawa M, Nitta S, Watanabe T, Otani S, Taniguchi M, Goto F, et al. Comprehensive analyses of mutations and hepatitis B virus integration in hepatocellular carcinoma with clinicopathological features. J Gastroenterol. 2016;51:473–486. - PubMed
-
- Anastas JN, Moon RT. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:11–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

