The Effect of Chronic Activation of the Novel Endocannabinoid Receptor GPR18 on Myocardial Function and Blood Pressure in Conscious Rats
- PMID: 27676325
- PMCID: PMC5209303
- DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000438
The Effect of Chronic Activation of the Novel Endocannabinoid Receptor GPR18 on Myocardial Function and Blood Pressure in Conscious Rats
Abstract
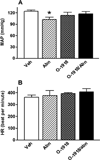
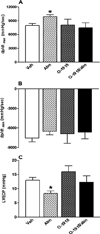
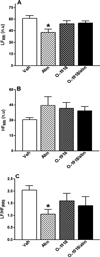
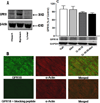
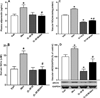
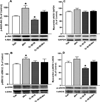
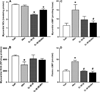
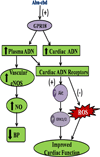
Although acute activation of the novel endocannabinoid receptor GPR18 causes hypotension, there are no reports on GPR18 expression in the heart or its chronic modulation of cardiovascular function. In this study, after demonstrating GPR18 expression in the heart, we show that chronic (2 weeks) GPR18 activation with its agonist abnormal cannabidiol (abn-cbd; 100 µg·kg·d; i.p) produced hypotension, suppressed the cardiac sympathetic dominance, and improved left ventricular (LV) function (increased the contractility index dp/dtmax and reduced LV end-diastolic pressure, LVEDP) in conscious rats. Ex vivo studies revealed increased: (1) cardiac and plasma adiponectin (ADN) levels; (2) vascular (aortic) endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, (3) vascular and serum nitric oxide (NO) levels; (4) myocardial and plasma cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels; (5) phosphorylation of myocardial protein kinase B (Akt) and extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) along with reduced myocardial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in abn-cbd treated rats. These biochemical responses contributed to the hemodynamic responses and were GPR18-mediated because concurrent treatment with the competitive GPR18 antagonist (O-1918) abrogated the abn-cbd-evoked hemodynamic and biochemical responses. The current findings present new evidence for a salutary cardiovascular role for GPR18, mediated, at least partly, via elevation in the levels of adiponectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pertwee RG, Howlett AC, Abood ME, Alexander SP, Di Marzo V, Elphick MR, Greasley PJ, Hansen HS, Kunos G, Mackie K, Mechoulam R, Ross RA. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: beyond CB(1) and CB(2) Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Dec;62(4):588–631. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jarai Z, Wagner JA, Varga K, Lake KD, Compton DR, Martin BR, Zimmer AM, Bonner TI, Buckley NE, Mezey E, Razdan RK, Zimmer A, Kunos G. Cannabinoid-induced mesenteric vasodilation through an endothelial site distinct from CB1 or CB2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Nov 23;96(24):14136–14141. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Offertaler L, Mo FM, Batkai S, Liu J, Begg M, Razdan RK, Martin BR, Bukoski RD, Kunos G. Selective ligands and cellular effectors of a G protein-coupled endothelial cannabinoid receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;63(3):699–705. - PubMed
-
- Begg M, Mo FM, Offertaler L, Batkai S, Pacher P, Razdan RK, Lovinger DM, Kunos G. G protein-coupled endothelial receptor for atypical cannabinoid ligands modulates a Ca2+- dependent K+ current. J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 14;278(46):46188–46194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

