Tau downregulates BDNF expression in animal and cellular models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 27676333
- PMCID: PMC5159317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.08.020
Tau downregulates BDNF expression in animal and cellular models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
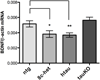
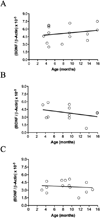
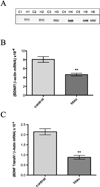
In Alzheimer's disease, soluble tau accumulates and deposits as neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). However, a precise toxic mechanism of tau is not well understood. We hypothesized that overexpression of wild-type tau downregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a neurotrophic peptide essential for learning and memory. Two transgenic mouse models of human tau expression and human tau (hTau40)-transfected human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells were used to examine the effect of excess or pathologically modified wild-type human tau on BDNF expression. Both transgenic mouse models, with or without NFTs, as well as hTau40-SH-SY5Y cells significantly downregulated BDNF messenger RNA compared with controls. Similarly, transgenic mice overexpressing amyloid-β (Aβ) significantly downregulated BDNF expression. However, when crossed with tau knockout mice, the resulting animals exhibited BDNF levels that were not statistically different from wild-type mice. These results demonstrate that excess or pathologically modified wild-type human tau downregulates BDNF and that neither a mutation in tau nor the presence of NFTs is required for toxicity. Moreover, our findings suggest that tau at least partially mediates Aβ-induced BDNF downregulation. Therefore, Alzheimer's disease treatments targeting Aβ alone may not be effective without considering the impact of tau pathology on neurotrophic pathways.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid-β; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Tau; Tauopathy; Transgenic mice.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
STATEMENT: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
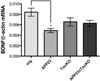
References
-
- Alderson RF, Alterman AL, Barde YA, Lindsay RM. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron. 1990;5(3):297–306. - PubMed
-
- Alonso AC, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Alzheimer’s disease hyperphosphorylated tau sequesters normal tau into tangles of filaments and disassembles microtubules. Nature medicine. 1996;2(7):783–787. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature. 1997;389:856–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

