Complement C3 inhibitor Cp40 attenuates xenoreactions in pig hearts perfused with human blood
- PMID: 27677785
- PMCID: PMC5358808
- DOI: 10.1111/xen.12262
Complement C3 inhibitor Cp40 attenuates xenoreactions in pig hearts perfused with human blood
Abstract
Background: The complement system plays a crucial role in acute xenogeneic reactions after cardiac transplantation. We used an ex vivo perfusion model to investigate the effect of Cp40, a compstatin analog and potent inhibitor of complement at the level of C3.
Methods: Fifteen wild-type pig hearts were explanted, cardiopleged, and reperfused ex vivo after 150 minutes of cold ischemia. Hearts were challenged in a biventricular working heart mode to evaluate cardiac perfusion and function. In the treatment group (n=5), the complement cascade was blocked at the level of C3 using Cp40, using diluted human blood. Untreated human and porcine blood was used for controls.
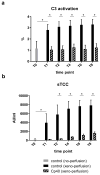
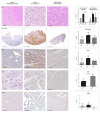
Results: Throughout the perfusion, C3 activation was inhibited when Cp40 was used (mean of all time points: 1.11 ± 0.34% vs 3.12 ± 0.48% control activation; P<.01). Compared to xenoperfused controls, the cardiac index improved significantly in the treated group (6.5 ± 4.2 vs 3.5 ± 4.8 mL/min/g; P=.03, 180 minutes perfusion), while the concentration of lactate dehydrogenase as a maker for cell degradation was reduced in the perfusate (583 ± 187 U/mL vs 2108 ± 1145 U/mL, P=.02). Histological examination revealed less hemorrhage and edema, and immunohistochemistry confirmed less complement fragment deposition than in untreated xenoperfused controls.
Conclusions: Cp40 efficiently prevents C3 activation of the complement system, resulting in reduced cell damage and preserved function in wild-type porcine hearts xenoperfused ex vivo. We suggest that this compstatin analog, which blocks all main pathways of complement activation, could be a beneficial perioperative treatment in preclinical and in future clinical xenotransplantation.
Keywords: complement; compstatin; ex vivo; heart; xenotransplantation.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
J.D.L. is the founder of Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, which is developing complement inhibitors for clinical applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple genetically modified GTKO/hCD46/HLA-E/hβ2-mg porcine hearts are protected from complement activation and natural killer cell infiltration during ex vivo perfusion with human blood.Xenotransplantation. 2018 Sep;25(5):e12390. doi: 10.1111/xen.12390. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Xenotransplantation. 2018. PMID: 29536572
-
Expression of human CD59 in transgenic pig organs enhances organ survival in an ex vivo xenogeneic perfusion model.Transplantation. 1996 May 27;61(10):1513-21. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199605270-00018. Transplantation. 1996. PMID: 8633381
-
Complement inhibition with an anti-C5 monoclonal antibody prevents acute cardiac tissue injury in an ex vivo model of pig-to-human xenotransplantation.Transplantation. 1995 Dec 15;60(11):1194-202. Transplantation. 1995. PMID: 8525509
-
[Xenotransplantation].Chirurg. 1996 Apr;67(4):324-30. Chirurg. 1996. PMID: 8646917 Review. German.
-
Complement inhibition in pre-clinical models of periodontitis and prospects for clinical application.Semin Immunol. 2016 Jun;28(3):285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Semin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27021500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Triple-fusion protein (TriFu): A potent, targeted, enzyme-like inhibitor of all three complement activation pathways.J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):105784. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105784. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38401844 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in platelet aggregometers to study platelet function and coagulation dysregulation in xenotransplantation.Xenotransplantation. 2021 Jan;28(1):e12645. doi: 10.1111/xen.12645. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Xenotransplantation. 2021. PMID: 32945034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel complement C3 inhibitor CP40-KK protects against experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension via an inflammasome NLRP3 associated pathway.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 16;22(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04741-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38365806 Free PMC article.
-
The complex functioning of the complement system in xenotransplantation.Xenotransplantation. 2019 Jul;26(4):e12517. doi: 10.1111/xen.12517. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Xenotransplantation. 2019. PMID: 31033064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-mediated rejection in xenotransplantation: Can it be prevented or reversed?Xenotransplantation. 2023 Jul-Aug;30(4):e12816. doi: 10.1111/xen.12816. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Xenotransplantation. 2023. PMID: 37548030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- COWAN PJ, D’APICE AJ. Complement activation and coagulation in xenotransplantation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2009;87:203–208. - PubMed
-
- EKSER B, EZZELARAB M, HARA H, et al. Clinical xenotransplantation: the next medical revolution? Lancet. 2012;379:672–683. - PubMed
-
- SAHU A, KAY BK, LAMBRIS JD. Inhibition of human complement by a C3-binding peptide isolated from a phage-displayed random peptide library. J Immunol. 1996;157:884–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous