High reward expectancy during methylphenidate depresses the dopaminergic response to gain and loss
- PMID: 27677943
- PMCID: PMC5390715
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsw124
High reward expectancy during methylphenidate depresses the dopaminergic response to gain and loss
Abstract
Dopamine plays an important role in goal-directed behavior, through its modulatory influence on striatal neurons. It is unclear whether tonic dopamine levels, which regulate the vigor of acting, interact with the phasic dopamine response to reward that drives instrumental behavior. In a randomized placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers, we show that methylphenidate, a drug that increases tonic dopamine levels, systematically reduced striatal phasic BOLD responses to gain and loss in a gambling task as measured with fMRI. It also increased response vigor and reward expectancy-related BOLD signals in the ventral striatum. These findings suggest that striatal tonic dopamine levels constitute an average reward expectation signal that modulates the phasic dopaminergic response to reward. This offers opportunities for treatment of behavioral disorders associated with abnormal reward sensitivity.
Keywords: Pharmacological fMRI; dopamine; feedback; gambling.
© The Author (2016). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

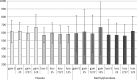
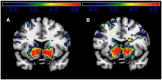
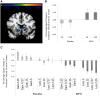
References
-
- Advokat C. (2010). What are the cognitive effects of stimulant medications? Emphasis on adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(8), 1256–66. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli F., Strafella A.P. (2014). Behavioral disorders in Parkinson’s disease: the role of dopamine. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, 20(Suppl 1), S10–2. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu J.M., Gainetdinov R.R. (2011). The physi ology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacological Review, 63(1), 182–217. - PubMed
-
- Bond A., Lader M. (1974). The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. British Journal of Medical Psychology, 47, 211–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

