Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Defense Response of Wheat against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici
- PMID: 27678307
- PMCID: PMC5039691
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34261
Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Defense Response of Wheat against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Defense Response of Wheat against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 22;6:38464. doi: 10.1038/srep38464. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28004734 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
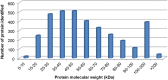
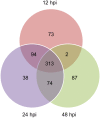
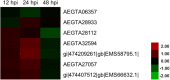
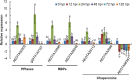
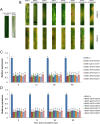
Wheat stripe rust, caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst), is considered one of the most aggressive diseases to wheat production. In this study, we used an iTRAQ-based approach for the quantitative proteomic comparison of the incompatible Pst race CYR23 in infected and non-infected leaves of the wheat cultivar Suwon11. A total of 3,475 unique proteins were identified from three key stages of interaction (12, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation) and control groups. Quantitative analysis showed that 530 proteins were differentially accumulated by Pst infection (fold changes >1.5, p < 0.05). Among these proteins, 10.54% was classified as involved in the immune system process and stimulus response. Intriguingly, bioinformatics analysis revealed that a set of reactive oxygen species metabolism-related proteins, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases (PPIases), RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), and chaperonins was involved in the response to Pst infection. Our results were the first to show that PPIases, RBPs, and chaperonins participated in the regulation of the immune response in wheat and even in plants. This study aimed to provide novel routes to reveal wheat gene functionality and better understand the early events in wheat-Pst incompatible interactions.
Figures



References
-
- Hovmoller M. S. et al. Diversity of Puccinia striiformis on Cereals and Grasses. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49, 197–217 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Kolmer J. A., Ordonez M. E. & Groth J. V. The Rust Fungi. In: eLS (ed^(eds). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd (2009).
-
- Quirino B. F. et al. Proteomic approaches to study plant-pathogen interactions. Phytochemistry 71, 351–362 (2010). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

