Exploring the metabolic syndrome: Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease
- PMID: 27678349
- PMCID: PMC5016366
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7660
Exploring the metabolic syndrome: Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease
Abstract
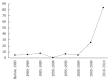
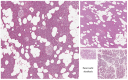
After the first description of fatty pancreas in 1933, the effects of pancreatic steatosis have been poorly investigated, compared with that of the liver. However, the interest of research is increasing. Fat accumulation, associated with obesity and the metabolic syndrome (MetS), has been defined as "fatty infiltration" or "nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease" (NAFPD). The term "fatty replacement" describes a distinct phenomenon characterized by death of acinar cells and replacement by adipose tissue. Risk factors for developing NAFPD include obesity, increasing age, male sex, hypertension, dyslipidemia, alcohol and hyperferritinemia. Increasing evidence support the role of pancreatic fat in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, MetS, atherosclerosis, severe acute pancreatitis and even pancreatic cancer. Evidence exists that fatty pancreas could be used as the initial indicator of "ectopic fat deposition", which is a key element of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and/or MetS. Moreover, in patients with fatty pancreas, pancreaticoduodenectomy is associated with an increased risk of intraoperative blood loss and post-operative pancreatic fistula.
Keywords: Fatty pancreas; Metabolic syndrome; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease; Pancreatic cancer; Pancreatic fat; Pancreatic fatty infiltration; Pancreatic fatty replacement; Pancreatic lipomatosis; Pancreatic steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet n° 311, 2011-01, cited 2016-06-03. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J; IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome--a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–1062. - PubMed
-
- Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease; pp. 1428–1441.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

