Upregulation of MiR-196a promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27kip1 in laryngeal cancer
- PMID: 27678369
- PMCID: PMC5039793
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-016-0100-9
Upregulation of MiR-196a promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27kip1 in laryngeal cancer
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidence has confirmed that miR-196a plays a critical role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression in a variety of cancers. It has been demonstrated that miR-196a is highly up-regulated in laryngeal cancer by miRNA profiling analysis. However, the functional mechanism of miR-196a in laryngeal cancer remains unclear. This study aims to explore the mechanism of miR-196a in laryngeal cancer.
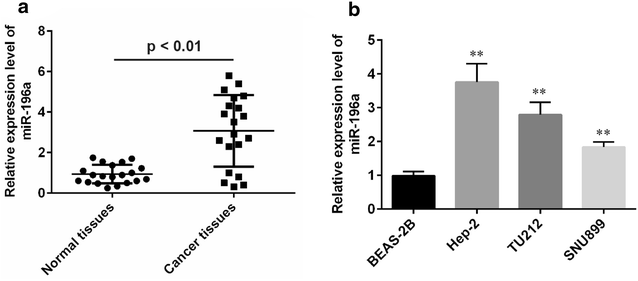
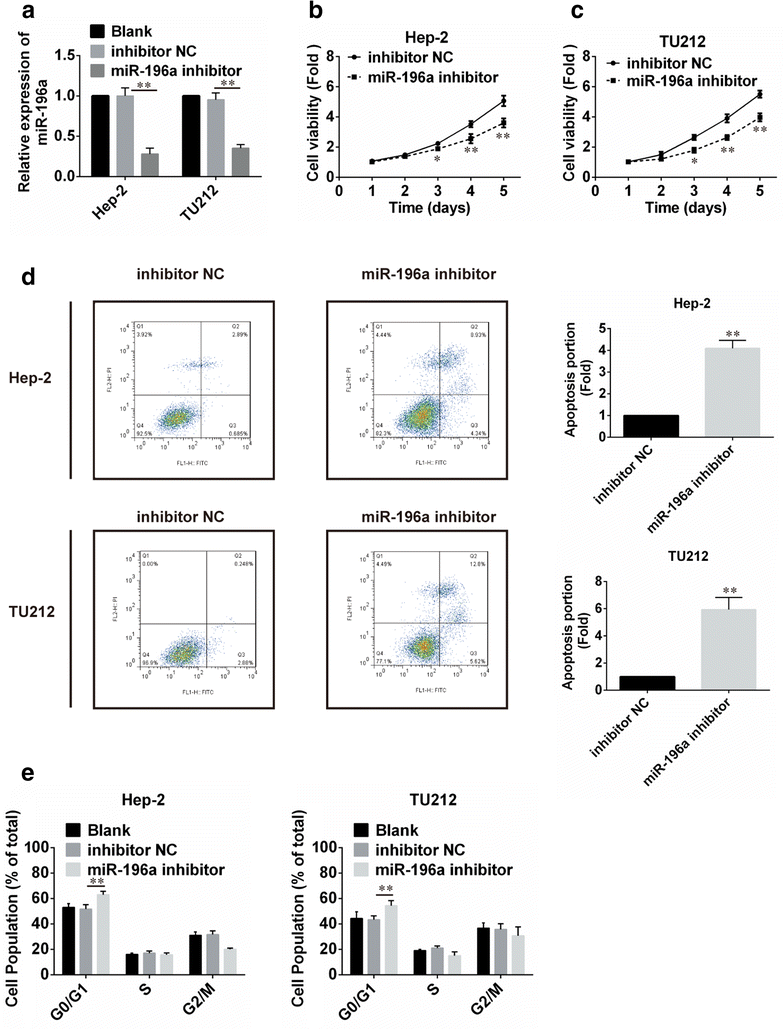
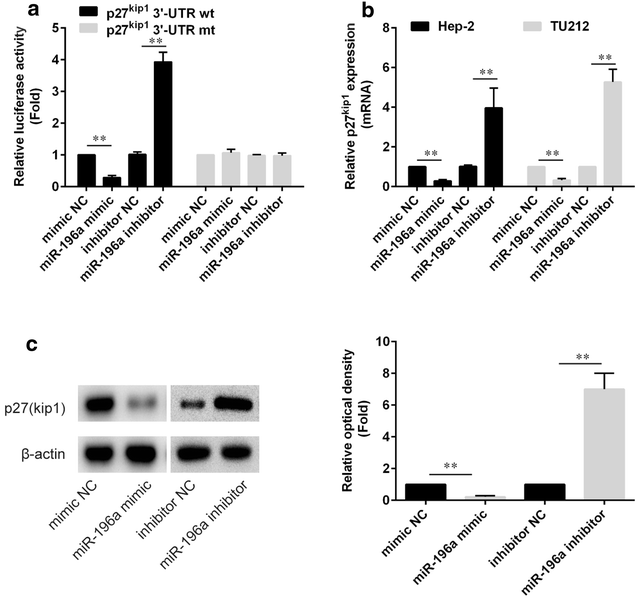
Methods: In the present study, we conducted qPCR analysis of miR-196a expression in human laryngeal cancer and showed that miR-196a was overexpressed in tumor-derived samples and laryngeal cancer cell lines compared with matched normal controls. Further functional analysis of miR-196a demonstrated that the inhibition of miR-196a could inhibit laryngeal cell-cycle progression and proliferation in vitro. Luciferase reporter assay and western blot confirmed that miR-196a directly targeted p27kip1. Moreover, in order to investigate whether miR-196a regulated cell growth in laryngeal cancer cells by targeting p27kip1, rescue studies were performed in laryngeal cancer cells.
Results: Results showed that overexpression of p27kip1 rescue decreased cell proliferation caused by miR-196a inhibitors. A negative relation between miR-196a and p27kip1 expression in laryngeal cancer tissues were also noted by further analyses.
Conclusions: The present study showed that miR-196a was upregulated in laryngeal cancer and promoted cell proliferation by downregulating p27kip1 in laryngeal cancer. However, further studies are needed to verify this finding.
Keywords: Laryngeal cancer; miR-196a; p27kip1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MiR-196a is upregulated in gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27(kip1).Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Apr;11(4):842-52. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-1015. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22343731
-
miR-196a-mediated downregulation of p27kip1 protein promotes prostate cancer proliferation and relates to biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy.Prostate. 2020 Sep;80(12):1024-1037. doi: 10.1002/pros.24036. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Prostate. 2020. PMID: 32628792
-
MicroRNA-196a post-transcriptionally upregulates the UBE2C proto-oncogene and promotes cell proliferation in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2015 Aug;34(2):877-83. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4049. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26062455
-
microRNA-196a Overexpression Inhibits Apoptosis in Hemin-Induced K562 Cells.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Feb;39(2):235-243. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5061. Epub 2020 Jan 8. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31913716
-
The role of microRNA-196a in tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and prognosis.Tumour Biol. 2016 Dec;37:15457–15466. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5430-2. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27752997 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-140 and miR-196a as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Jul 1;21(7):1913-1918. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.7.1913. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32711415 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Gain-of-Function Screening to Identify miRNAs Involved in Paclitaxel Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 20;25(24):13630. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413630. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769392 Free PMC article.
-
miR-196a Promotes Proliferation of Mammary Epithelial Cells by Targeting CDKN1B.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;13(23):3682. doi: 10.3390/ani13233682. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067033 Free PMC article.
-
miR-196a regulates the proliferation, invasion and migration of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells by targeting ANXA1.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jun;17(6):5201-5209. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10186. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31186736 Free PMC article.
-
Footprints of microRNAs in Cancer Biology.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 19;9(10):1494. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101494. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sethi N, Rafferty A, Rawnsley T, Jose J. Short, sharp shock public health campaign had limited impact on raising awareness of laryngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;16:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Witold F, Bhattacharyya SN, Nahum S. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(2):102–114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

