A Cytosolic Amphiphilic α-Helix Controls the Activity of the Bile Acid-sensitive Ion Channel (BASIC)
- PMID: 27679529
- PMCID: PMC5114408
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756437
A Cytosolic Amphiphilic α-Helix Controls the Activity of the Bile Acid-sensitive Ion Channel (BASIC)
Abstract
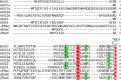
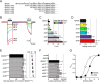
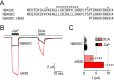
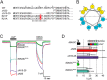
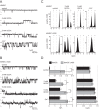
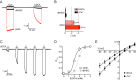
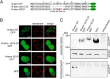
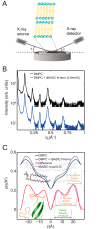
The bile acid-sensitive ion channel (BASIC) is a member of the degenerin/epithelial Na+ channel (Deg/ENaC) family of ion channels. It is mainly found in bile duct epithelial cells, the intestinal tract, and the cerebellum and is activated by alterations of its membrane environment. Bile acids, one class of putative physiological activators, exert their effect by changing membrane properties, leading to an opening of the channel. The physiological function of BASIC, however, is unknown. Deg/ENaC channels are characterized by a trimeric subunit composition. Each subunit is composed of two transmembrane segments, which are linked by a large extracellular domain. The termini of the channels protrude into the cytosol. Many Deg/ENaC channels contain regulatory domains and sequence motifs within their cytosolic domains. In this study, we show that BASIC contains an amphiphilic α-helical structure within its N-terminal domain. This α-helix binds to the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane and stabilizes a closed state. Truncation of this domain renders the channel hyperactive. Collectively, we identify a cytoplasmic domain, unique to BASIC, that controls channel activity via membrane interaction.
Keywords: BASIC; BLINaC; Deg/ENaC; X-ray scattering; Xenopus; amphiphilic helix; bile acid; cholesterol; ion channel; patch clamp.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Kellenberger S., and Schild L. (2002) Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol. Rev. 82, 735–767 - PubMed
-
- Kellenberger S., and Schild L. (2015) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCI. structure, function, and pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels and the epithelial Na+ channel. Pharmacol. Rev. 67, 1–35 - PubMed
-
- Waldmann R., Champigny G., Bassilana F., Heurteaux C., and Lazdunski M. (1997) A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 386, 173–177 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

