Uncertainties in target volume delineation in radiotherapy - are they relevant and what can we do about them?
- PMID: 27679540
- PMCID: PMC5024655
- DOI: 10.1515/raon-2016-0023
Uncertainties in target volume delineation in radiotherapy - are they relevant and what can we do about them?
Abstract
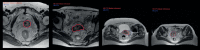
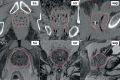
Background: Modern radiotherapy techniques enable delivery of high doses to the target volume without escalating dose to organs at risk, offering the possibility of better local control while preserving good quality of life. Uncertainties in target volume delineation have been demonstrated for most tumour sites, and various studies indicate that inconsistencies in target volume delineation may be larger than errors in all other steps of the treatment planning and delivery process. The aim of this paper is to summarize the degree of delineation uncertainties for different tumour sites reported in the literature and review the effect of strategies to minimize them.
Conclusions: Our review confirmed that interobserver variability in target volume contouring represents the largest uncertainty in the process for most tumour sites, potentially resulting in a systematic error in dose delivery, which could influence local control in individual patients. For most tumour sites the optimal combination of imaging modalities for target delineation still needs to be determined. Strict use of delineation guidelines and protocols is advisable both in every day clinical practice and in clinical studies to diminish interobserver variability. Continuing medical education of radiation oncologists cannot be overemphasized, intensive formal training on interpretation of sectional imaging should be included in the program for radiation oncology residents.
Keywords: delineation uncertainties; imaging; interobserver variability; target volume; training.
Figures
References
-
- Pötter R, Georg P, Dimopoulos JC, Grimm M, Berger D, Nesvacil N. et al. Clinical outcome of protocol based image (MRI) guided adaptive brachytherapy combined with 3D conformal radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2011;100:116–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van de Steene J, Linthout N, De Mey J, Vinh-Hung V, Claassens C, Noppen M. et al. Definition of gross tumor volume in lung cancer: Inter-observer variability. Radiother Oncol. 2002;62:37–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee WR, Roach M III, Michalski J, Moran B, Beyer D. Interobserver variability leads to significant differences in quantifiers of prostate implant adequacy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;54:457–61. - PubMed
-
- Kim RY, McGinnis SL, Spencer SA, Meredith RF, Jennelle RLS, Salter MM. Conventional four-field pelvic radiotherapy technique without computed tomography-treatment planning in cancer of the cervix: potential geographic miss and its impact on pelvic control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:109–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

