A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
- PMID: 27679787
- PMCID: PMC5035439
- DOI: 10.5812/atr.29042
A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
Abstract
Introduction: The fracture of front teeth is one of the routine presentations of traumatic injuries. The treatment of a fractured tooth involving the pulp includes root canal therapy and post placement followed by core build-up or by the extraction of the fractured tooth if it is not restorable.
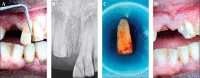
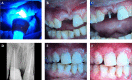
Case presentation: We report a case of an adult male who had traumatized both his maxillary central incisors following a blow experienced during domestic violence. He had lost a fractured fragment of the right central incisor, while the left incisor had complicated fractures with fragments retained attached to the soft tissue. Following radiovisiography (RVG), both incisors were conservatively treated in a single visit by reattachment and post and core techniques.
Conclusions: The treatment reported for reattachment of the tooth fractures and post and core techniques are reasonably easy while providing immediate and lasting results in patients' regaining of social confidence and functionality.
Keywords: Composite Resins; Esthetics; Tooth Fractures; Wounds and Injuries.
Figures
References
-
- Olsburgh S, Jacoby T, Krejci I. Crown fractures in the permanent dentition: pulpal and restorative considerations. Dent Traumatol. 2002;18(3):103–15. - PubMed
-
- Simonsen R, Thompson VP, Barrark G. Etched cast restorations:clinical and laboratory technique. Chicago: Quintessence; 1985. pp. 150–1.
-
- Tennery TN. The fractured tooth reunited using the acid-etch bonding technique. Tex Dent J. 1978;96(8):16–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
