Pannexin3 inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory response by suppressing NF-κB signalling pathway in human dental pulp cells
- PMID: 27679980
- PMCID: PMC5323855
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12988
Pannexin3 inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory response by suppressing NF-κB signalling pathway in human dental pulp cells
Abstract
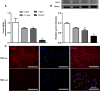
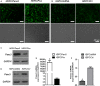
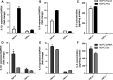
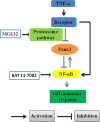
Human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) play a crucial role in dental pulp inflammation. Pannexin 3 (Panx3), a member of Panxs (Pannexins), has been recently found to be involved in inflammation. However, the mechanism of Panx3 in human dental pulp inflammation remains unclear. In this study, the role of Panx3 in inflammatory response was firstly explored, and its potential mechanism was proposed. Immunohistochemical staining showed that Panx3 levels were diminished in inflamed human and rat dental pulp tissues. In vitro, Panx3 expression was significantly down-regulated in HDPCs following a TNF-α challenge in a concentration-dependent way, which reached the lowest level at 10 ng/ml of TNF-α. Such decrease could be reversed by MG132, a proteasome inhibitor. Unlike MG132, BAY 11-7082, a NF-κB inhibitor, even reinforced the inhibitory effect of TNF-α. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were used to investigate the role of Panx3 in inflammatory response of HDPCs. TNF-α-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, were significantly lessened when Panx3 was overexpressed in HDPCs. Conversely, Panx3 knockdown exacerbated the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, Western blot, dual-luciferase reporter assay, immunofluorescence staining, qRT-PCR and ELISA results showed that Panx3 participated in dental pulp inflammation in a NF-κB-dependent manner. These findings suggested that Panx3 has a defensive role in dental pulp inflammation, serving as a potential target to be exploited for the intervention of human dental pulp inflammation.
Keywords: NF-κB; Pannexin3; TNF-α; human dental pulp cells; proteasome; pulpitis.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Wnt5a promotes inflammatory responses via nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in human dental pulp cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 25;289(30):21028-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546523. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24891513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Catechins reduce inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated dental pulp cells by inhibiting activation of the NF-κB pathway.Oral Dis. 2020 May;26(4):815-821. doi: 10.1111/odi.13290. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Oral Dis. 2020. PMID: 31999881
-
Semaphorin3A released from human dental pulp cells inhibits the increase in interleukin-6 and CXC chemokine ligand 10 production induced by tumor necrosis factor-α through suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Jan;45(1):238-244. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11466. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 32926524
-
The role of NF-kappaB in the inflammatory processes related to dental caries, pulpitis, apical periodontitis, and periodontitis-a narrative review.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 29;12:e17953. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17953. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39221277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics to the Understanding of TNF-α Signaling.J Proteome Res. 2017 Jan 6;16(1):14-33. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00728. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 27762135 Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt4 prevents apoptosis and inflammation of dental pulp cells induced by LPS by inhibiting the IKK/NF‑κB pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Dec 23;25(2):75. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11774. eCollection 2023 Feb. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36684653 Free PMC article.
-
Different expression patterns of inflammatory cytokines induced by lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli or Porphyromonas gingivalis in human dental pulp stem cells.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Apr 12;22(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02161-x. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35413908 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopene Ameliorates Transplant Arteriosclerosis in Vascular Allograft Transplantation by Regulating the NO/cGMP Pathways and Rho-Associated Kinases Expression.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3128280. doi: 10.1155/2016/3128280. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 28050227 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 May;22(5):2558-2568. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13491. Epub 2018 Mar 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29502358 Free PMC article.
-
A Review in Research Progress Concerning m6A Methylation and Immunoregulation.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;10:922. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00922. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31080453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Renard E, Gaudin A, Bienvenu G, et al Immune cells and molecular networks in experimentally induced pulpitis. J Dent Res. 2016; 95: 196–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

