Effects of Renal Impairment on Steady-State Plasma Concentrations of Rivastigmine: A Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Capsule and Patch Formulations in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 27681702
- PMCID: PMC5075013
- DOI: 10.1007/s40266-016-0405-y
Effects of Renal Impairment on Steady-State Plasma Concentrations of Rivastigmine: A Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Capsule and Patch Formulations in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Introduction: The glomerular filtration rate (GFR), a measure of renal function, decreases by approximately 10 mL/min every 10 years after the age of 40 years, which could lead to the accumulation of drugs and/or renal toxicity. Pharmacokinetic studies of drugs excreted both renally and non-renally are desirable in patients with impaired renal function, defined by parameters including estimated GFR (eGFR) and creatinine clearance (CLCR).
Objective: We describe here a population pharmacokinetic analysis of the possible effects of renal impairment on steady-state plasma concentrations of rivastigmine and its metabolite NAP226-90 after rivastigmine patch (5 cm2 [4.6 mg/24 h], 10 cm2 [9.5 mg/24 h], 15 cm2 [13.3 mg/24 h], and 20 cm2 [17.4 mg/24 h]) and capsule (1.5, 3, 4.5, and 6 mg/12 h) treatment in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
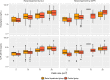
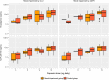
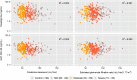
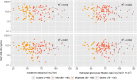
Methods: The data used to conduct the current pharmacokinetic analysis were obtained from the pivotal phase III, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, parallel-group study (IDEAL). One blood sample was collected from each patient at steady-state to measure plasma concentrations of rivastigmine and NAP226-90 using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. The steady-state plasma concentrations of rivastigmine and NAP226-90 were plotted against CLCR and eGFR data, and boxplots were constructed after stratification by renal function.
Results: The two groups (mild/no renal impairment vs. moderate/severe/end-stage renal impairment) showed comparable demographic covariates for all patch sizes and capsule doses. No correlation was observed between CLCR or eGFR and plasma concentrations of rivastigmine or NAP226-90. Boxplots of concentrations of rivastigmine or NAP226-90 for each dose largely overlapped for patch and capsule. Additionally, model-based estimates of plasma concentrations adjusted for body weight yielded similar results.
Conclusion: The results of this study show that renal function does not affect rivastigmine or NAP226-90 steady-state plasma concentrations, and no dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment is required. CLINICALTRIALS.GOV: NCT00099242.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical StandardsFundingThis study was funded by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland.Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of interestGilbert Lefèvre and Francesca Callegari are employees of Novartis and as such may be eligible for Novartis stock and stock options. Sandro Gsteiger and Yuan Xiong were employees of Novartis at the time of the research and analysis and as such may have been eligible for Novartis stock and stock options. None of the authors are Fellows of the American College of Clinical Pharmacology (FCP).Research Involving Human ParticipantsThe protocol, informed consent form, any amendments, and other information given to patients and caregivers were reviewed by an Institutional Review Board or Independent Ethics Committee for each center. The study was conducted according to the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, as revised in 2000.Informed ConsentInformed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures
References
-
- Bell JS, Blacker N, Leblanc VT, Alderman CP, Phillips A, Rowett D, et al. Prescribing for older people with chronic renal impairment. Aust Fam Physician. 2013;42:24–28. - PubMed
-
- Glassock RJ. The GFR decline with aging: a sign of normal senescence, not disease. Nephrol Times. 2009;9:6–8. doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000361312.27730.cc. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

