Effects of Sanguis Draconis on Perforator Flap Survival in Rats
- PMID: 27681718
- PMCID: PMC6273294
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21101262
Effects of Sanguis Draconis on Perforator Flap Survival in Rats
Abstract
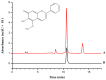
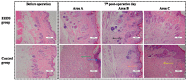
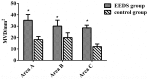
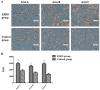
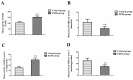
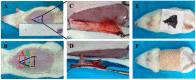
Sanguis draconis, a resin known to improve blood circulation, relieve pain, stimulate tissue regeneration, and heal wounds, is widely used in clinical practice. In this study, we prepared an ethanol extract of sanguis draconis (EESD) containing 75.08 mg/g of dracorhodin. The experiment was carried out on 20 rats that were divided into two groups, a control group (n = 10) and an EESD group (n = 10). All the rats underwent a perforator flap surgery, after which post-operative abdominal compressions of EESD were given to the EESD group for seven days, while the control group received saline. Flap survival percentages were determined after seven days, and were found to be significantly higher in the EESD group than in the control group. Results of laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) showed that perforator flaps in the EESD group had higher perfusion values than those of the control group. The flap tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, followed by immunohistochemical evaluation. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) expression and micro-vessel development markedly increased in the EESD group, while malondialdehyde (MDA) levels decreased. This is the first study to investigate the effect of sanguis draconis on perforator flap survival. Our results demonstrate that sanguis draconis can improve perforator flap survival in rats by promoting microvessel regeneration and blood perfusion.
Keywords: dracorhodin; flap survival; microvessels; perforator flaps; perfusion; sanguis draconis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effect of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase on Multiterritory Perforator Flap Survival in Rats.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016 Nov;32(9):643-649. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1584808. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016. PMID: 27367807
-
[Effects of pretreatment with dimethyloxalylglycine on the survival of multi-territory perforator flap in rat and related mechanism].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016 Jul 20;32(7):396-401. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.07.003. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27464629 Chinese.
-
Effects of bradykinin on the survival of multiterritory perforator flaps in rats.World J Surg Oncol. 2019 Feb 27;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1570-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30813916 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Draconis Sanguis-containing serum on NGF, BDNF, CNTF, LNGFR, TrkA, GDNF, GAP-43 and NF-H expressions in Schwann cells].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;40(7):1392-5. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26281567 Chinese.
-
The protective effect of Irisin against ischemia-reperfusion injury after perforator flap grafting in rats.Injury. 2018 Dec;49(12):2147-2153. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.09.054. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Injury. 2018. PMID: 30293870
Cited by
-
Neferine Protects against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rats by Suppressing NLRP3-Mediated Inflammasome Activation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 May 8;2021:6654954. doi: 10.1155/2021/6654954. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34046147 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Obesity Effect of Shenheling Extract (SHLE) Fermented with Lactobacillus fermentum grx08.Foods. 2022 Apr 23;11(9):1221. doi: 10.3390/foods11091221. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35563944 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Protective Mechanisms of Bioactive Phytochemicals in Flap Surgery.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 25;13:864351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.864351. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35548348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Butylphthalide Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Multiterritory Perforator Flap Survival.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 29;11:612932. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.612932. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamdi M., Craggs B., Stoel A.M., Hendrickx B., Zeltzer A. Superior epigastric artery perforator flap: Anatomy, clinical applications, and review of literature. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014;30:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Ammar A.D., Bissell M.B., Alejandro M.M., Steven F.M. Anatomical Study of the Princeps Pollicis Artery Perforator Flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016;76:564–568. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

