Integration of complex data sources to provide biologic insight into pulmonary vascular disease (2015 Grover Conference Series)
- PMID: 27683602
- PMCID: PMC5019078
- DOI: 10.1086/686995
Integration of complex data sources to provide biologic insight into pulmonary vascular disease (2015 Grover Conference Series)
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Pulm Circ. 2017 Apr-Jun;7(2):559. doi: 10.1177/2045893217706334. Pulm Circ. 2017. PMID: 28597768 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
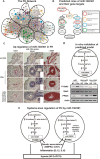
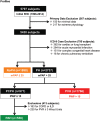
The application of complex data sources to pulmonary vascular diseases is an emerging and promising area of investigation. The use of -omics platforms, in silico modeling of gene networks, and linkage of large human cohorts with DNA biobanks are beginning to bear biologic insight into pulmonary hypertension. These approaches to high-throughput molecular phenotyping offer the possibility of discovering new therapeutic targets and identifying variability in response to therapy that can be leveraged to improve clinical care. Optimizing the methods for analyzing complex data sources and accruing large, well-phenotyped human cohorts linked to biologic data remain significant challenges. Here, we discuss two specific types of complex data sources-gene regulatory networks and DNA-linked electronic medical record cohorts-that illustrate the promise, challenges, and current limitations of these approaches to understanding and managing pulmonary vascular disease.
Keywords: biorepository; computational network modeling; electronic medical record; genomics; pulmonary vascular disease; systems biology.
Figures
References
-
- National Institutes of Health. Redefining pulmonary hypertension through pulmonary vascular disease phenomics: clinical centers (CC) (U01). http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/rfa-files/RFA-HL-14-027.html. Published November 25, 2013. Accessed October 3, 2015.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

