Systematic reviews and meta-analyses in spine surgery, neurosurgery and orthopedics: guidelines for the surgeon scientist
- PMID: 27683675
- PMCID: PMC5039866
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2414-469X.2015.06.01
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses in spine surgery, neurosurgery and orthopedics: guidelines for the surgeon scientist
Abstract
The research evidence in the realm of surgery is expanding at a rapid pace, and thus corresponds with an increasing need to critically appraise and synthesize the available literature. Particularly in fields such as spine surgery, neurosurgery and orthopedics which traditionally have little Class I randomized clinical data, reviews are important to pool the available evidence on clinical questions which are otherwise difficult to answer. Whilst systematic reviews and meta-analyses have the potential to provide critical and updated surgical evidence to guide clinical decisions, poorly performed analyses and misinterpretation of such reviews may have a detrimental effect on patient care and outcomes. We present a summary of the critical steps in performing a systematic review and meta-analysis, allowing the surgeon scientist to better interpret and perform their own systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
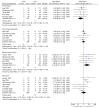
Keywords: Systematic review; academic surgery; clinical outcomes; evidence; forest plot; heterogeneity; meta-analysis; spine; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Oxman AD, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH. Users' guides to the medical literature. VI. How to use an overview. Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1994;272:1367-71. - PubMed
-
- Murad MH, Montori VM. Synthesizing evidence: shifting the focus from individual studies to the body of evidence. JAMA 2013;309:2217-8. - PubMed
-
- Phan K, Thayaparan GK, Mobbs RJ. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion - systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg 2015;29:705-11. - PubMed
-
- Phan K, Rao PJ, Kam AC, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 2015;24:1017-30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
