Learning the trajectory of a moving visual target and evolution of its tracking in the monkey
- PMID: 27683886
- PMCID: PMC5133302
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00519.2016
Learning the trajectory of a moving visual target and evolution of its tracking in the monkey
Abstract
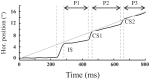
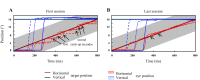
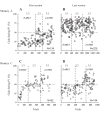
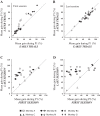
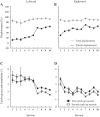
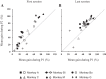
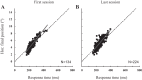
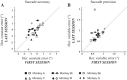
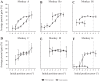
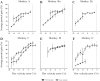
An object moving in the visual field triggers a saccade that brings its image onto the fovea. It is followed by a combination of slow eye movements and catch-up saccades that try to keep the target image on the fovea as long as possible. The accuracy of this ability to track the "here-and-now" location of a visual target contrasts with the spatiotemporally distributed nature of its encoding in the brain. We show in six experimentally naive monkeys how this performance is acquired and gradually evolves during successive daily sessions. During the early exposure, the tracking is mostly saltatory, made of relatively large saccades separated by low eye velocity episodes, demonstrating that accurate (here and now) pursuit is not spontaneous and that gaze direction lags behind its location most of the time. Over the sessions, while the pursuit velocity is enhanced, the gaze is more frequently directed toward the current target location as a consequence of a 25% reduction in the number of catch-up saccades and a 37% reduction in size (for the first saccade). This smoothing is observed at several scales: during the course of single trials, across the set of trials within a session, and over successive sessions. We explain the neurophysiological processes responsible for this combined evolution of saccades and pursuit in the absence of stringent training constraints. More generally, our study shows that the oculomotor system can be used to discover the neural mechanisms underlying the ability to synchronize a motor effector with a dynamic external event.
Keywords: prediction; pursuit; saccade; synchronism; tracking.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Accardo AP, Pensiero S, Pozzo SDA, Perissutti P. Characteristics of horizontal smooth pursuit eye movements to sinusoidal stimulation in children of primary school age. Vision Res 35: 539–548, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Bahill AT. Modeling the smooth-pursuit eye-movement system. Automedica 19: 1–17, 2000.
-
- Bahill AT, Iandolo MJ, Troost BT. Smooth pursuit eye movements in response to unpredictable target waveforms. Vision Res 20: 923–931, 1980. - PubMed
-
- Barnes GR. Cognitive processes involved in smooth pursuit eye movements. Brain Cogn 68: 309–326, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Barnes GR, Collins S. Influence of predictability on control of extra-retinal components of smooth pursuit during prolonged 2D tracking. Exp Brain Res 233: 885–897, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

