Immunoproteomic analysis of house dust mite antigens reveals distinct classes of dominant T cell antigens according to function and serological reactivity
- PMID: 27684489
- PMCID: PMC5374056
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12829
Immunoproteomic analysis of house dust mite antigens reveals distinct classes of dominant T cell antigens according to function and serological reactivity
Abstract
Background: House dust mite (HDM) allergens are a common cause of allergy and allergic asthma. A comprehensive analysis of proteins targeted by T cells, which are implicated in the development and regulation of allergic disease independent of their antibody reactivity, is still lacking.
Objective: To comprehensively analyse the HDM-derived protein targets of T cell responses in HDM-allergic individuals, and investigate their correlation with IgE/IgG responses and protein function.
Methods: Proteomic analysis (liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry) of HDM extracts identified 90 distinct protein clusters, corresponding to 29 known allergens and 61 novel proteins. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 20 HDM-allergic individuals were stimulated with HDM extracts and assayed with a set of ~2500 peptides derived from these 90 protein clusters and predicted to bind the most common HLA class II types. 2D immunoblots were made in parallel to elucidate IgE and IgG reactivity, and putative function analyses were performed in silico according to Gene Ontology annotations.
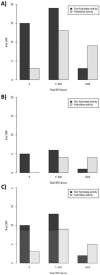
Results: Analysis of T cell reactivity revealed a large number of T cell epitopes. Overall response magnitude and frequency was comparable for known and novel proteins, with 15 antigens (nine of which were novel) dominating the total T cell response. Most of the known allergens that were dominant at the T cell level were also IgE reactive, as expected, while few novel dominant T cell antigens were IgE reactive. Among known allergens, hydrolase activity and detectable IgE/IgG reactivity are strongly correlated, while no protein function correlates with immunogenicity of novel proteins. A total of 106 epitopes accounted for half of the total T cell response, underlining the heterogeneity of T cell responses to HDM allergens.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: Herein, we define the T cell targets for both known allergens and novel proteins, which may inform future diagnostics and immunotherapeutics for allergy to HDM.
Keywords: T cell epitopes; allergens; house dust mite; proteomics.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Soyer OU, Akdis M, Ring J, Behrendt H, Crameri R, Lauener R, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of peripheral tolerance to allergens. Allergy. 2013;68:161–70. - PubMed
-
- Pernas M, Sanchez-Ramos I, Sanchez-Monge R, Lombardero M, Arteaga C, Castanera P, Salcedo G. Der p 1 and Der f 1, the highly related and major allergens from house dust mites, are differentially affected by a plant cystatin. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2000;30:972–8. - PubMed
-
- Deb R, Shakib F, Reid K, Clark H. Major house dust mite allergens Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus 1 and Dermatophagoides farinae 1 degrade and inactivate lung surfactant proteins A and D. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282:36808–19. - PubMed
-
- Machado DC, Horton D, Harrop R, Peachell PT, Helm BA. Potential allergens stimulate the release of mediators of the allergic response from cells of mast cell lineage in the absence of sensitization with antigen-specific IgE. European journal of immunology. 1996;26:2972–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

