Methods of milk expression for lactating women
- PMID: 27684560
- PMCID: PMC6457747
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006170.pub5
Methods of milk expression for lactating women
Abstract
Background: Breastfeeding is important, however not all infants can feed at the breast and methods of expressing milk need evaluation.
Objectives: To assess acceptability, effectiveness, safety, effect on milk composition, contamination and costs of methods of milk expression.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (21 March 2016), handsearched relevant journals and conference proceedings, and contacted experts in the field to seek additional published or unpublished studies. We also examined reference lists of all relevant retrieved papers.
Selection criteria: Randomised and quasi-randomised trials comparing methods at any time after birth.
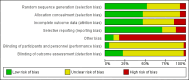
Data collection and analysis: Three review authors independently assessed trials for inclusion and risk of bias, extracted data and checked them for accuracy.
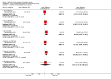
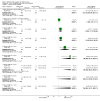
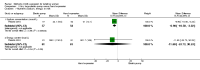
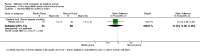
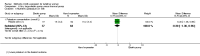
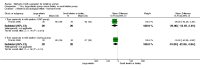
Main results: This updated review includes 41 trials involving 2293 participants, with 22 trials involving 1339 participants contributing data for analysis. Twenty-six of the trials referred to mothers of infants in neonatal units (n = 1547) and 14 to mothers of healthy infants at home (n = 730), with one trial containing mothers of both neonatal and healthy older infants (n = 16). Eleven trials compared one or more types of pump versus hand expression and 14 studies compared one type of pump versus another type of pump, with three of these studies comparing both hand expression and pump types. Twenty studies compared a specific protocol or adjunct behaviour including sequential versus simultaneous pumping protocols, pumping frequency, provision of an education and support intervention, relaxation, breast massage, combining hand expression with pumping and a breast cleansing protocol.Due to heterogeneity in participants, interventions, and outcomes measured or reported, we were unable to pool findings for most of the specified outcomes. It was not possible therefore to produce a 'Summary of findings' table in this update. Most of the included results were derived from single studies. Trials took place in 14 countries under a variety of circumstances and were published from 1982 to 2015. Sixteen of the 30 trials that evaluated pumps or products had support from the manufacturers. The risk of bias of the included studies was variable. Primary outcomesOnly one of the 17 studies examining maternal satisfaction/acceptability with the method or adjunct behaviour provided data suitable for analysis. In this study, self-efficacy was assessed by asking mothers if they agreed or disagreed with the following statement: 'I don't want anyone to see me (hand expressing/pumping)'. The study found that mothers who were using the electric pump were more likely to agree with the statement compared to mothers hand expressing, (mean difference (MD) 0.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.15 to 1.25; P = 0.01, participants = 68). Mothers who were hand expressing reported that the instructions for expression were clearer compared to the electric pump, (MD -0.40, 95% CI -0.75 to -0.05; P = 0.02, participants = 68). Descriptive reporting of satisfaction in the other studies varied in the measures used, did not indicate a clear preference for one pump type, although there was satisfaction with some relaxation and support interventions.We found no clinically significant differences between methods related to contamination of the milk that compared any type of pump to hand expression (risk ratio (RR) 1.13, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.61; P = 0.51, participants = 28), manual pump compared to hand expression, (MD 0.20, 95% CI -0.18 to 0.58; P = 0.30, participants = 142) a large electric pump compared to hand expression (MD 0.10, 95% CI -0.29 to 0.49; P = 0.61, participants = 123), or a large electric pump compared to a manual pump (MD -0.10, 95% CI -0.46 to 0.26; P = 0.59, participants = 141).The level of maternal breast or nipple pain or damage was similar in comparisons of a large electric pump to hand expression (MD 0.02, 95% CI -0.67 to 0.71; P = 0.96, participants = 68). A study comparing a manual and large electric pump, reported sore nipples in 7% for both groups and engorgement in 4% using a manual pump versus 6% using an electric pump; and in one study no nipple damage was reported in the hand-expression group, and one case of nipple damage in each of the manual pump and the large electric pump groups.One study examined adverse effects on infants, however as the infants did not all receive their mothers' expressed milk, we have not included the results. Secondary outcomesThe quantity of expressed milk obtained was increased, in some studies by a clinically significant amount, in interventions involving relaxation, music, warmth, massage, initiation of pumping, increased frequency of pumping and suitable breast shield size. Support programmes and simultaneous compared to sequential pumping did not show a difference in milk obtained. No pump consistently increased the milk volume obtained significantly.In relation to nutrient quality, hand expression or a large electric pump were found to provide higher protein than a manual pump, and hand expression provided higher sodium and lower potassium compared to a large electric pump or a manual pump. Fat content was higher with breast massage when pumping; no evidence of difference was found for energy content between methods.No consistent effect was found related to prolactin change or effect on oxytocin release with pump type or method. Economic aspects were not reported.
Authors' conclusions: The most suitable method for milk expression may depend on the time since birth, purpose of expression and the individual mother and infant. Low-cost interventions including initiation of milk expression sooner after birth when not feeding at the breast, relaxation, massage, warming the breasts, hand expression and lower cost pumps may be as effective, or more effective, than large electric pumps for some outcomes. Variation in nutrient content across methods may be relevant to some infants. Small sample sizes, large standard deviations, and the diversity of the interventions argue caution in applying these results beyond the specific method tested in the specific settings. Independently funded research is needed for more trials on hand expression, relaxation and other techniques that do not have a commercial potential.
Conflict of interest statement
Genevieve Becker works in the general area of infant and young child feeding, but is not specifically connected with the topic of this review. She is not in receipt of any financial relationship with any commercial entity.
In October 2012 Hazel A Smith registered as a PhD student to study the effects of infant's milk diet at two months of age on their body composition, growth and neurodevelopment in the first 2 years of life. Hazel is the Research Coordinator for the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit in Our Lady's Children's Hospital, Ireland. Hazel is not in receipt of any financial relationship with any commercial entity.
Fionnuala Cooney works as a Specialist in Public Health Medicine. She received no funds for work on this review, has no relationship to any commercial organisation involved in research on this topic, and has no known conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
























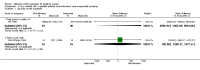







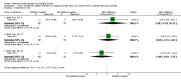




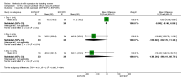


Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006170.pub4
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahmed 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ahmed A. Breastfeeding preterm infants: an educational program to support mothers of preterm infants in Cairo, Egypt. Pediatric Nursing 2008;34(2):125‐38. - PubMed
Auerbach 1990 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Auerbach KG. Sequential and simultaneous breast pumping: a comparison. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1990;27(3):257‐65. - PubMed
Bernabe‐Garcia 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bernabe‐Garcia M, Lopez‐Alarcon M, Villegar R, Rodriguez‐Cruz M, Jimenez‐Galicia C. Usefulness of four manual breast pumps for mothers after preterm delivery in a developing country. Unpublished manuscript. - PubMed
-
- Bernabe‐Garcia M, Lopez‐Alarcon M, Villegas‐Silva R, Rodriguez‐Cruz M, Jimenez‐Galicia C. Effectiveness of four manual breast pumps for mothers after preterm delivery in a developing country. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2012;31(1):63‐9. - PubMed
Boo 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Boo N, Nordiah AJ, Alfizah H, Nor‐Rohaini AH, Lim VK. Contamination of breast milk obtained by manual expression and breast pumps in mothers of very low birthweight infants. ACP Journal Club 2000;132(3):116. - PubMed
-
- Boo NY, Nordiah AJ, Alfizah H, Nor‐Rohaini AH, Lim VK. Contamination of breast milk obtained by manual expression and breast pumps in mothers of very low birthweight infants. Journal of Hospital Infection 2001;49(4):274‐81. - PubMed
Boutte 1985 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Boutte CA, Garza C, Kennard‐Fraley J, Stuff JE, O'Brian‐Smith E. Comparison of hand and electric operated breast pumps. Human Nutrition: Applied Nutrition 1985;39A:416‐30. - PubMed
Burton 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Burton P, Kennedy K, Ahluwalia J, Nicholl R, Lucas A, Fewtrell M. Randomized trial comparing the effectiveness of two electric breast pumps in the NICU. Journal of Human Lactation 2013;29(3):412‐9. - PubMed
-
- Burton PM, Kennedy K, Lucas A, Ahluwalla J, Nicholl R, Fewtrell M. Breast pump design and milk production: a randomised control trial. American Academy of Pediatrics Annual Meeting; 2010 October 2‐5; San Francisco, California, USA. 2010.
-
- Fewtrell M. Randomised trial comparing the efficacy of the ISIS Duo iQ electric breast pump and the Medela Symphony electric breast pump in mothers expressing breast milk for preterm infants. ClinicalTrials.gov (www.clinicaltrials.gov/) [accessed July 2010] 2009.
Costa 1989 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Costa KM. A comparison of colony counts of breast milk using two methods of breast cleansing. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1989;18:231‐6. - PubMed
De Carvalho 1985 {published data only}
-
- Carvalho M, Anderson DM, Giangreco A, Pittard WB. Frequency of milk expression and milk production by mothers of nonnursing premature neonates. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1985;139:483‐5. - PubMed
Feher 1989 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Feher S, Berger L, Johnson J, Wilde J. Increasing breast milk production for premature infants with a relaxation/imagery audiotape. Pediatrics 1989;83(1):57‐60. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2001a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Fewtrell M, Lucas P, Collier S, Lucas A. Randomized study comparing the efficacy of a novel manual breast pump with a mini‐electric breast pump in mothers of term infants. Journal of Human Lactation 2001;17(2):126‐31. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2001b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fewtrell MS, Lucas P, Collier S, Singhal A, Ahluwalia JS, Lucas A. Randomized trial comparing the efficacy of a novel manual breast pump with a standard electric breast pump in mothers who delivered preterm infants. Pediatrics 2001;107(6):1291‐7. - PubMed
Flaherman 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Flaherman VJ, Scott C, Gay B, Lee K, Newman TB. Randomized trial of electric breast pump use vs. hand expression in mothers of infants feeding poorly at 12‐36 hours. Pediatric Academic Societies' Annual Meeting; 2010 May 1‐4; Vancouver, Canada. 2010.
Francis 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Francis J. Maternal/infant lactation characteristics (MILC) study: a comparison of single electric pumping devices. Journal of Human Lactation 2008;24(1):107.
-
- Francis J, Bertz P, Wagoner C. The maternal/infant lactation characteristics (MILC) study: evaluation of three single electric pumping devices. Unpublished paper provided by study author J Francis.
Garza 1982 {published data only}
-
- Garza C, Johnson CA, Harrist R, Nichols BL. Effects of methods of collection and storage on nutrients in human milk. Early Human Development 1982;6:295‐303. - PubMed
Groh‐Wargo 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Groh‐Wargo S, Toth A, Mahoney K, Simonian S, Wasser T, Rose S. The utility of a bilateral breast pumping system for mothers of premature infants. Neonatal Network 1995;14:31‐6. - PubMed
Hayes 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hayes DK, Prince CB, Espinueva V, Fuddy LJ, Li R, Grummer‐Strawn LM. Comparison of manual and electric breast pumps among WIC women returning to work or school in Hawaii. Breastfeeding Medicine 2008;3(1):3‐10. - PubMed
Heon 2011 {published data only}
-
- Heon J, Goulet C, Garofalo C, Nuyt AM, Levy E. Interventions to promote breastmilk promotion in mothers of pre‐term infants. Western Journal of Nursing Research 2014;38(5):529‐52. - PubMed
-
- Heon M. Nursing Interventions Related to Breastfeeding in Preterm Infants. Montreal: University of Montreal, 2011.
-
- Heon M, Goulet C, Garofalo C, Nuyt AM, Levy E. Acceptability and feasibility of a breast milk expression education and support intervention in mothers of preterm infants. Advances in Neonatal Care 2014;14(4):E9‐E19. - PubMed
Hill 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hill PD, Aldag JC, Chatterton RT. Breastfeeding experience and milk weight in lactating mothers pumping for preterm infants. Birth 1999;26(4):233‐8. - PubMed
-
- Hill PD, Aldag JC, Chatterton RT. Effects of pumping style on milk production in mothers of non‐nursing preterm infants. Journal of Human Lactation 1999;15(3):209‐16. - PubMed
-
- Hill PD, Aldag JC, Chatterton RT. Initiation and frequency of pumping and milk production in mothers of non‐nursing preterm infants. Journal of Human Lactation 2001;17(1):9‐13. - PubMed
-
- Hill PD, Aldag JC, Chatterton RT. Initiation of pumping and milk weight in mothers of non‐nursing preterm infants. Integrating Population Outcomes, Biological Mechanisms and Research Methods in the Study of Human Milk and Lactation. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 2005:267‐9.
-
- Hill PD, Aldag JC, Chatterton RT. The effect of sequential and simultaneous breast pumping on milk volume and prolactin levels: a pilot study. Journal of Human Lactation 1996;12(3):193‐9. - PubMed
Hopkinson 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hopkinson J, Heird W. Maternal response to two electric breast pumps. Breastfeeding Medicine 2009;4(1):17‐23. - PubMed
Jayamala 2015 {published data only}
Jones 2001 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Keith 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Keith DR, Weaver BS, Vogel RL. The effect of music‐based listening interventions on the volume, fat content, and caloric content of breast milk‐produced by mothers of premature and critically ill infants. Advances in Neonatal Care 2012;12(2):112‐9. - PubMed
Lussier 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lussier M, Brownell E, Proulx T, Bielecki D, Marinelli K, Bellini S, et al. Daily breast mik volume in mothers of very low birth weight neonates: a repeated measures randomized trial of hand expression versus electric expression. Breastfeeding Medicine 2014;9(Suppl 1):S‐1. - PubMed
-
- Lussier MM, Brownell E, Proulx T, Bielecki D, Marinelli K, Bellini S, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing seven days of exclusive hand expression with exclusive electric expression to measure milk volumes in the first 28 postpartum days in mothers of very low birth infants. 17th Conference of the International Society for Research in Human Milk and Lactation (ISRHML); 2014 Oct 23‐27; Kiawah Island, South Carolina, USA. 2014.
-
- Lussier MM, Brownell EA, Proulx TA, Bielecki DM, Marinelli KA, Bellini SL, et al. Daily breastmilk volume in mothers of very low birth weight neonates: A repeated‐measures randomized trial of hand expression versus electric breast pump expression. Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(6):312‐7. - PubMed
Mangel 2015 {published data only}
-
- Mangel L, Ovental A, Batscha N, Arnon M, Yarkoni I, Dollberg S. Higher fat content in breastmilk expressed manually: a randomized trial. Breastfeeding Medicine : the Official Journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(7):352‐4. - PubMed
Meier 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Engstrom JL, Meier PP, Jegier B, Motykowski JE, Zuleger JL. Comparison of milk output from the right and left breasts during simultaneous pumping in mothers of very low birthweight infants. Breastfeeding Medicine 2007;2(2):83‐91. - PubMed
-
- Meier PP, Engstrom JL, Hurst NM, Ackerman B, Allen M, Motykowski JE, et al. A comparison of the efficiency, efficacy, comfort, and convenience of two hospital‐grade electric breast pumps for mothers of very low birthweight infants. Breastfeeding Medicine 2008;3(3):141‐50. - PubMed
-
- Meier PP, Hurst N, Rodriguez N, Ackerman B, Howard K, Allen M, et al. Comfort and effectiveness of the Symphony breast pump for mothers of preterm infants; comparison of three suction pumps. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 2004;554:321‐3. - PubMed
Meier 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Mersmann 1993 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mersmann CA. Therapeutic Touch and Milk Letdown in Mothers of Non‐nursing Preterm Infants [PhD Thesis]. New York: New York University, 1993.
Parker 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Parker LA, Sullivan S, Krueger C. Effect of early breast milk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low birth weight infants: a pilot study. American Academy of Pediatrics Annual Meeting; 2010 October 2‐5; San Francisco, California, USA. 2010. - PubMed
-
- Parker LA, Sullivan S, Krueger C, Kelechi T, Mueller M. Effect of early breast milk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low birth weight infants: A pilot study. Journal of Perinatology 2012;32(3):205‐9. - PubMed
Paul 1996 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Paul VK, Singh M, Deorari AK, Pacheco J, Teneja U. Manual and pump methods of expression of breast milk. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1996;63:87‐92. - PubMed
Pessoto 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pessoto MA, Marba STM. Is a high quality expressed breast milk, according to expression method, possible for the premature baby in a third world country?. Pediatric Academic Societies' 2010 Annual Meeting; 2010 May 1‐4; Vancouver, Canada. 2010.
Pinelli 2001 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Callen J, Pinelli J, Atkinson S, Saigal S. Qualitative analysis of barriers to breastfeeding in very low‐birthweight infants in the hospital and post discharge. Advances in Neonatal Care 2005;5:93‐103. - PubMed
-
- Pinelli J, Atkinson SA, Saigal S. Randomized trial of breastfeeding support in very low‐birth‐weight infants. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2001;155:548‐53. - PubMed
-
- Pinelli J, Saigal S, Atkinson SA. Effect of breast milk consumption and selected variables on neurodevelopmental outcomes at 6 and 12 months of age in very low birth weight infants. Advances in Neonatal Care 2003;3(2):76‐87. - PubMed
Pittard 1991 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Pittard WB, Geddes KM, Brown S, Hulsey TC. Bacterial contamination of human milk: container type and method of expression. American Journal of Perinatology 1991;8(1):25‐7. - PubMed
-
- Pittard WB, Geddes KM, Brown S, Mintz S, Hulsey TC. Bacterial contamination of human milk. Pediatric Research 1989;25:122A. - PubMed
Prime 2010 {published data only}
-
- Prime DK. Dynamics of Milk Flow and Milk Ejection During Breast Expression in Women. PhD Thesis, University of Western Australia. Perth: University of Western Australia, 2010.
-
- Prime DK, Geddes DG, Spatz DL, Trengove NJ, Hartmann PE. The effect of breastshield size and anatomy on milk removal in women. Journal of Human Lactation 2010;26(4):433.
Prime 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Prime DK, Garbin CP, Hartmann PE, Kent JC. A comparison of simultaneous and sequential breast expression in women. Journal of Human Lactation 2010;26(4):433.
Rasmussen 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Rasmussen K, Dieterich C, Zelek S, Altabet J, Kjolhede C. Interventions to increase the duration of breastfeeding in obese mothers: the Bassett Improving Breastfeeding Study. Breastfeeding Medicine 2011;6(2):69‐75. - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen KM, Dieterich CM, Zelek ST, Altabet JD, Kjolhede CL. Interventions to increase the duration of breastfeeding in obese mothers. Poster abstract at 2010 ISRHML conference. Journal of Human Lactation 2010;26:430.
Slusher 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Slusher T, Slusher IL, Biomdo M, Bode‐Thomas F, Curtis BA, Meier PP. Electric breast pump use increases maternal milk volume in African nurseries. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2007;53(2):125‐30. - PubMed
-
- Slusher TM, Slusher IL, Biomdo M, Bode‐Thomas F, Redd BC, Meier PP. Electric breast pump use increases maternal milk volume and decreases time to onset of adequate maternal milk volume in African nurseries. Pediatric Research 2004;55 Suppl:32.
Stellwagen 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Chan CS, Stellwagen LM, Vaucher YE, Montminy TD, Kim JH. Hand expression combined with pumping does not change the nutrient content of human milk from mothers of very low birthweight infants. Pediatric Academic Societies' 2010 Annual Meeting; 2010 May 1‐4; Vancouver, Canada. 2010.
-
- Stellwagen LM, Vaucher YE, Chan CS, Kim JH. Does hand expression improve human milk production in pump dependent mothers of VLBW infants?. Pediatric Academic Societies' 2010 Annual Meeting; 2010 May 1‐4; Vancouver, Canada. 2010.
Stutte 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stutte PC, Bowles BC, Morman GY. The effects of breast massage on volume and fat content of human milk. Genesis 1988;10(2):22‐5.
Vasan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Vasan U, Joseph S, Mathews J, Engstrom J, Meier P. Maternal milk volume (MMV) and milk transfer (MT) for low birth weight (LBW: <2500G) infants in Ecuador: comparison of electric breast pump and hand expression. 11th Conference of the International Society for Research in Human Milk and Lactation (ISRHML); 2004. 2004.
Yiğit 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yiğit F, Cigdem Z, Temizsoy E, Cingi ME, Korel O, Yildirim E, et al. Does warming the breasts affect the amount of breastmilk production?. Breastfeeding Medicine 2012;7(6):487‐8. - PubMed
Zinaman 1992 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Zinaman MJ, Hughes V, Queenan JT, Labbok MH, Albertson B. Acute prolactin and oxytocin responses and milk yield to infant suckling and artificial methods of expression in lactating women. Pediatrics 1992;89(3):437‐40. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alekseev 1998 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Alekseev NP, Ilyin VI, Yaroslavski VK, Gaidukov SN, Tikhonova TK, Specivcev YA, et al. Compression stimuli increase the efficacy of breast pump function. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 1998;7:131‐9. - PubMed
Batista 2014 {published data only}
-
- Batista dos Santos HA, Muniz de Moura MA, Souza MA, Nohama P. Evaluation of massage techniques and pumping in the treatment of breast engorgement by thermography [Evaluacion de las tecnicas de masaje y bombeo en el tratamiento de la congestion mamaria por termografia]. Revista Latino‐Americana de Enfermagem (RLAE) 2014;22(2):277‐85. - PMC - PubMed
Chapman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chapman DJ, Young S, Ferris AM, Perez‐Escamilla R. Impact of breast pumping on lactogenesis stage II after cesarean delivery: a randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics 2001;107:E94. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2006 {published data only}
Flores‐Huerta 1995 {published data only}
-
- Flores‐Huerta S, Sanchez‐Hidalgo VM, Matute G, Contreras‐Lemus J, Villalpando S. Volume and composition comparison of human foremilk extracted with manual or electrical pump [Comparacion del volumen y composicion del calostro extraido con una bomba manual o electrica]. Boletin Medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico 1995;52(8):465‐70.
Forster 2011 {published data only}
-
- Forster DA, McEgan K, Ford R, Moorhead A, Opie G, Walker S, et al. Diabetes and antenatal milk expressing: a pilot project to inform the development of a randomised controlled trial. Midwifery 2011;27(2):209‐14. - PubMed
Fujimoto 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fujimoto S, Yokoo K, Nakagomi S, Murakami M. Mothers' experiences of expressing breast milk for neonates in the NICU ‐ difference between hand and electric breast pump expression. Journal of Health Sciences, Hiroshima University 2006;6(1):65‐70.
Green 1982 {published data only}
-
- Green D, Moye L, Schreiner RL, Lemons JA. The relative efficacy of four methods of human milk expression. Early Human Development 1982;6(2):153‐9. - PubMed
Junior 2008 {published data only}
-
- Junior WS, Martinez FE. Effect of intervention on the rates of breastfeeding of very low birth weight newborns. Neonatal Intensive Care 2008;21(2):37‐41.
Kent 2003 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Kent JC, Ramsey DT, Doherty D, Larsson M, Hartmann PE. Responses of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric pump. Journal of Human Lactation 2003;19(2):179‐86. - PubMed
Kent 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kent JC, Mitoulas LR, Cregan MD, Geddes DT, Larsson M, Doherty DA, et al. Importance of vacuum for breastmilk expression. Breastfeeding Medicine 2008;2(1):11‐9. - PubMed
Kimani‐Murage 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kimani‐Murage EW, Kyobutungi C, Ezeh AC, Wekesah F, Wanjohi M, Muriuki P, et al. Effectiveness of personalised, home‐based nutritional counselling on infant feeding practices, morbidity and nutritional outcomes among infants in Nairobi slums: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. Trials [Electronic Resource] 2013;14:445. - PMC - PubMed
Lang 1994 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Lang S, Lawrence CJ, Orme RL. Sodium in hand and pump expressed human breast milk. Early Human Development 1994;38(2):131‐8. - PubMed
Lewis 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Lewis SL. Effect of Electric Breast Pump on Breastfeeding Duration and Exclusivity in Working Utah Woman, Infants and Children Program participants [dissertation]. Utah: College of Health, University of Utah, 2005.
Mennella 2010a {published data only}
Mennella 2010b {published data only}
Morton 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Morton J, Hall JY, Wong RJ, Thairu L, Benitz WE, Rhine WD. Combining hand techniques with electric pumping increases milk production in mothers of preterm infants. Journal of Perinatology 2009;29:757‐64. - PubMed
-
- Morton J, Wong RJ, Hall JY, Pang WW, Lai C, Hartmann P, et al. Combining hand techniques with electric pumping increases the caloric content of milk in mothers of preterm infants. Journal of Perinatology 2012;32:791‐6. - PubMed
NCT00393640 {published and unpublished data}
-
- NCT00393640. Early and regular breast milk expression to help establish lactation after delivery: a randomized controlled trial. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00393640 Date first received: 27 October 2006.
NCT01802047 {published data only}
-
- Dollberg S. Milk volume production in mothers of preterm infants: electric pumping modalities. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01802047 Date first received: 19 February 2013.
Ohyama 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ohyama M, Watabe H, Hayasaka Y. Manual expression and electric breast pumping in the first 48 h after delivery. Pediatrics International: Official Journal of the Japan Pediatric Society 2010; Vol. 52, issue 1:39‐43. - PubMed
-
- Ohyama M, Watabe H, Hayasaka Y. Which is more effective, manual‐ or electric‐expression in the first 48 hours after delivery in a setting of mother‐infant separation? Preliminary report. Breastfeeding Medicine 2007;2(3):179.
Pepino 2008 {published data only}
Pound 2015 {published data only}
Slusher 2012 {published data only}
-
- Slusher TM, Slusher IL, Keating EM, Curtis BA, Smith EA, Orodriyo E, et al. Comparison of maternal milk (breastmilk) expression methods in an African nursery. Breastfeeding Medicine 2012;7(2):107‐11. - PubMed
Thompson 1997 {published data only}
-
- Thompson N, Pickler RH, Munro C, Shotwell J. Contamination in expressed breast milk following breast cleansing. Journal of Human Lactation 1997;13(2):127‐30. - PubMed
Waller 1946 {published data only}
-
- Waller H. The early failure of breast feeding. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1946;21:1‐12. - PubMed
Williams 1985 {published data only}
-
- Williams AF, Akinkugbe FM, Baum JD. A comparison of two methods of milk sampling for calculating the fat intake of breast‐fed babies. Human Nutrition. Clinical Nutrition 1985;39:193‐202. - PubMed
Yoshidome 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yoshidome A, Hayashi I. Comparison of triglyceride and calcium levels before and after lactation and breast massage. International Confederation of Midwives 30th Triennial Congress. Midwives: Improving Women’s Health; 2014 June 1‐4; Prague, Czech Republic. 2014:P174.
Zhen 1990 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Zhen H, Qian A. Breast massage to promote milk secretion for pregnant and parturient women. Chinese Journal of Nursing 1990;25(9):454‐5. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Raguindin 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- ACTRN12614000218695. Kangaroo mother care and its lactogenic effects. anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=365839&isReview... Date first received: 28 February 2014.
-
- Raguindin PF, Uy ME, Dumalag JA. Prolactin level and breast milk volume among mothers of low birth weight infants admitted to Level II neonatal intensive care unit who underwent kangaroo mother care. Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(Suppl 1):S‐4.
Yu 2014 {unpublished data only}
-
- Yu R. Philips AVENT Relaxation Study. http://www.healthcare.philips.com/pwc_hc/main/shared/Assets/Documents/av... (accessed May 12 2014).
References to ongoing studies
Fewtrell NCT02128295 {published data only}
-
- NCT02128295. Trial of two electric breast pumps in mothers of term infants. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02128295 Date first received: 29 April 2014.
Parker NCT01892085 {published data only}
-
- NCT01892085. Early initiation of milk expression in mothers of very low birth weight infants. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01892085 Date first received: June 28 2013.
Sahler NCT01893047 {published data only}
-
- NCT01893047. Effect of quiet or listening to music while breastfeeding on the production and lipid and sodium content of the milk. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01893047 Date first received: June 20 2013.
Sisk NCT01167517 {published data only}
-
- NCT01167517. Lactation education study in mothers of very low birth weight infants. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01167517 Date first received: 20 July 2010.
Additional references
AAP 2012
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Policy Statement: breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012;129:e827‐e841. - PubMed
Acuña‐Muga 2014
-
- Acuña‐Muga J, Ureta‐Velasco N, Cruz‐Bértolo J, Ballesteros‐López R, Sánchez‐Martínez R, Miranda‐Casabona E, et al. Volume of milk obtained in relation to location and circumstances of expression in mothers of very low birth weight infants. Journal of Human Lactation 2014;30:41‐6. - PubMed
Arnold 1990
-
- Arnold L. Clinical uses of donor milk. Journal of Human Lactation 1990;6:132‐3. - PubMed
Asquith 1984
-
- Asquith MT, Pedrotti PW, Harrod JR, Stevenson DK, Sunshine P. The bacterial content of breast milk after the early initiation of expression using a standard technique. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 1984;3(1):104‐7. - PubMed
Auerbach 1981
-
- Auerbach KG, Avery JL. Induced lactation. A study of adoptive nursing by 240 women. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1981;135(4):340‐3. - PubMed
Bachrach 2003
-
- Bachrach V, Schwarz E, Bachrach L. Breastfeeding and the risk of hospitalization for respiratory disease in infancy: a meta‐analysis. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2003;157:237‐43. - PubMed
Ball 1999
-
- Ball T, Wright A. Health care cost of formula‐feeding in the first year of life. Pediatrics 1999;103:870‐6. - PubMed
Bartick 2010
-
- Bartick M, Reinhold A. The burden of suboptimal breastfeeding in the United States: a pediatric cost analysis. Pediatrics 2010;125(5):1048‐56. - PubMed
Becker 2008b
-
- Becker GE. Assessing Health Worker Performance in Assisting a Mother to Learn Skills of Hand Expression of Breast Milk. PhD thesis, Medical Education Unit, School of Medicine, University of Leeds 2008. [http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/1231]
Bier 2002
-
- Bier J, Oliver T, Ferguson A, Vohr B. Human milk improves cognitive and motor development of premature infants during infancy. Journal of Human Lactation 2002;18:361‐7. - PubMed
Biervliet 2001
-
- Biervliet FP, Maguiness SD, Hay DM, Killick SR, Atkin SL. Induction of lactation in the intended mother of a surrogate pregnancy: case report. Human Reproduction 2001;16(3):581‐3. - PubMed
Binns 2006
-
- Binns CW, Win NN, Zheo Y, Scott JA. Trends in the expression of breastmilk 1993‐2003. Breastfeeding Review 2006;14(3):5‐9. - PubMed
Black 2013
-
- Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta, ZA, Christian, P, Onis M, et al. Maternal and child under nutrition and overweight in low‐income and middle‐income countries. Lancet 2013;382:427‐51. - PubMed
Blaymore 2002
-
- Blaymore Bier J, Oliver T, Ferguson A, Vohr B. Human milk reduces outpatient upper respiratory symptoms in premature infants during their first year of life. Journal of Perinatology 2002;22:354‐9. - PubMed
Blenkharn 1989
-
- Blenkharn JI. Infection risks from electrically operated breast pumps. Journal of Hospital Infection 1989;13(1):27‐31. - PubMed
BLISS 2008
-
- BLISS. Breastfeeding or Expressing for a Sick or Premature Baby: An Overview of 500 Women's Experiences. London: BLISS, 2008.
Brown 2005
-
- Brown SL, Bright RA, Dwyer DE, Foxman B. Breast pump adverse events: reports to the Food and Drug Administration. Journal of Human Lactation 2005;21(2):169‐74. - PubMed
Buchko 1994
-
- Buchko B, Pugh L, Bishop B, Cochran J, Smith L, Lerew D. Comfort measures in breastfeeding, primiparous women. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1994;23(1):46‐52. - PubMed
Buckley 2009
CDC 2007
-
- Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity. Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of pediatric overweight. Research to Practice Series. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2007:1‐8.
Chen 2004
-
- Chen A, Rogan W. Breastfeeding and the risk of postneonatal death in the United States. Pediatrics 2004;113(5):e435‐9. - PubMed
Chen 2012
-
- Chen PG, Johnson LW, Rosenthal MS. Sources of education about breastfeeding and breast pump use: what effect do they have on breastfeeding duration? An analysis of the Infant Feeding Practices Survey II. Maternal and Child Health Journal 2012;16:1421‐30. - PubMed
Clemons 2010
-
- Clemons SN, Amir LH. Breastfeeding women's experience of expressing: a descriptive study. Journal of Human Lactation 2010;26(3):258‐65. - PubMed
Cohen 1995
-
- Cohen R, Mrtek MB, Mrtek RG. Comparison of maternal absenteeism and infant illness rates among breast‐feeding and formula‐feeding women in two corporations. American Journal of Health Promotion 1995;10:148‐53. - PubMed
COMA 1981
-
- COMA. The Collection and Storage of Human Milk; Reports of a Working Party on Human Milk Banks, Panel on Child Nutrition. Reports on Health and Social Subjects Number 22. London: Department of Health and Social Security Committee on Medical Aspects of Food Policy, 1981. - PubMed
D'Amico 2004
-
- D'Amico C, DiNardo C, Krystofiak S. Preventing contamination of breast pump kit attachments in the NICU. Journal of Perinatal Neonatal Nursing 2003;17(2):150‐7. - PubMed
Donovan 2012
Duijts 2010
-
- Duijts L, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Moll HA. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics 2010;126(1):e18‐e25. - PubMed
Egnell 1956
-
- Egnell E. Mechanics of different methods of emptying the female breast. Journal of the Swedish Medical Association 1956;40:1‐8.
Fein 2008
-
- Fein SB, Grummer‐Strawn LM, Raju TN. Infant feeding and care practices in the United States: results from the infant feeding practices Study II. Pediatrics 2008;122(Suppl 2):S25‐S27. - PubMed
Felice 2015
-
- Felice JP, Rasmussen KM. Breasts, pumps and bottles, and unanswered questions. Breastfeeding Medicine 2015;10(9):1‐4. - PubMed
Ferris 1984
-
- Ferris AM, Jensen RG. Lipids in human milk: a review. 1: sampling, determination, and content. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1984;3(1):108‐22. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2004
-
- Fewtrell M. The long‐term benefits of having been breast‐fed. Current Paediatrics 2004;14(2):97‐103.
Fewtrell 2016
-
- Fewtrell MS, Kennedy K, Ahluwalia JS, Nicholl R, Lucas A, Burton PM. Predictors of expressed breast milk volume in mothers expressing milk for their preterm infant. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2016; Vol. epub ahead of print. [DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2015-308321] - DOI - PubMed
Foda 2004
-
- Foda MI, Kawashima T, Nakamura S, Kobayashi M, Oku T. Composition of milk obtained from unmassaged versus massaged breasts of lactating mothers. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2004;38(5):484‐7. - PubMed
Forster 2015
Furman 2002
-
- Furman L, Minich N, Hack M. Correlates of lactation in mothers of very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2002;109(4):e57. - PubMed
Gdalevich 2001
-
- Gdalevich M, Mimouni D, Mimouni M. Breast‐feeding and the risk of bronchial asthma in childhood: a systematic review with meta‐analysis of prospective studies. Journal of Pediatrics 2001;139:261‐6. - PubMed
Geraghty 2005
-
- Geraghty SR, Khoury JC, Kalkwarf HJ. Human milk pumping rates of mothers of singletons and mothers of multiples. Journal of Human Lactation 2005;21(4):413‐20. - PubMed
Geraghty 2012
Gerstein 1994
-
- Gerstein H. Cow’s milk exposure and type 1 diabetes mellitus. A critical overview of the clinical literature. Diabetes Care 1994;17:13‐9. - PubMed
Hamosh 1984
-
- Hamosh M, Berkow S, Bitman J, Freed G, Happ B, Jones JB, et al. Handling and storage of human milk specimens for research. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1984;3(2):284‐9. - PubMed
Hartmann 1985
-
- Hartmann PE, Rattigan S, Saint L, Supriyana O. Variation in the yield and composition of human milk. Oxford Reviews of Reproductive Biology 1985;7:118‐67. - PubMed
Higgins 2006
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.6 [updated September 2006]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2006. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hill 1996
-
- Hill P, Aldag J, Chatterton R. The effect of sequential and simultaneous breast pumping on milk volume and prolactin levels: a pilot study. Journal of Human Lactation 1996;12(3):193‐9. - PubMed
Hills‐Bonczyk 1993
-
- Hills‐Bonczyk SG, Avery MD, Savik K, Potter S, Duckett LJ. Women's experiences with combining breast‐feeding and employment. Journal of Nurse‐Midwifery 1993;38(5):257‐66. - PubMed
Hopkinson 1988
-
- Hopkinson JM, Schanler RJ, Garza C. Milk production by mothers of premature infants. Pediatrics 1988;81(6):815‐20. - PubMed
Horta 2013a
-
- Horta BL, Victora CG. Long‐term effects of breastfeeding: a systematic review. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2013.
Horta 2013b
-
- Horta BL, Victora CG. Short‐term effects of breastfeeding: a systematic review on the benefits of breastfeeding on diarrhoea and pneumonia mortality. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2013.
Howie 1990
Hylander 1998
-
- Hylander M, Strobino D, Dhanireddy R. Human milk feedings, and infection among very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1998;102:e38. - PubMed
Ip 2007
Jegier 2010
Jiang 2015
Johns 2013
Karimi 2013
-
- Karimi M, Eslami Z, Shamsi F, Moradi J, Ahmadi AY, Baghianimoghadam B. The effect of educational intervention on decreasing mothers’ expressed breast milk bacterial contamination whose infants are admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Research in Health Sciences 2013;13(1):43‐7. - PubMed
Kramer 2008
-
- Kramer MS, Aboud F, Mironova E, Vanilovich I, Platt RW, Matush L, et al. Breastfeeding and child cognitive development: new evidence from a large randomized trial. Archives of General Psychiatry 2008;65(5):578‐84. - PubMed
Labayen 2012
-
- Labayen I, Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Loit HM, Harro J, Villa I, et al. Exclusive breastfeeding duration and cardiorespiratory fitness in children and adolescents. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2012;95(2):498‐505. - PubMed
Labiner‐Wolfe 2008
-
- Labiner‐Wolfe J, Fein SB, Shealy KR, Wang C. Prevalence of breast milk expression and associated factors. Pediatrics 2008;122(Suppl 2):S63‐S68. - PubMed
Lucas 1990
-
- Lucas A, Cole T. Breast milk and neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 1990;336:1519‐23. - PubMed
Marild 2004
-
- Marild S, Hansson S, Jodal U, Oden A, Svedberg K. Protective effect of breastfeeding against urinary tract infection. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 2004;93:164‐8. - PubMed
McCrory 2011
-
- McCrory C, Layte R. The effect of breastfeeding on children's educational test scores at nine years of age: results of an Irish cohort study. Social Science and Medicine 2011;72(9):1515‐21. - PubMed
McGuire 2003
McInnes 2015
Meserve 1982
-
- Meserve Y. Management of postpartum breast engorgement in non‐breastfeeding women by mechanical extraction of milk. Journal of Nurse Midwifery 1982;27:3‐8. - PubMed
Mitoulas 2002a
-
- Mitoulas L, Lai C, Gurrin L, Larsson M, Hartmann P. Effect of vacuum profile on breast milk expression using an electric breast pump. Journal of Human Lactation 2002;18(4):353‐60. - PubMed
Mitoulas 2002b
-
- Mitoulas LR, Lai CT, Gurrin LC, Larsson M, Hartmann PE. Efficacy of breast milk expression using an electric breast pump. Journal of Human Lactation 2002;18(4):344‐52. - PubMed
Newell 2004
-
- Newell ML. HIV transmission through breastfeeding:a review of available evidence. Geneva: WHO/UNICEF/UNAIDS, 2004.
NICE 2006
-
- NICE: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Postnatal care: national cost impact report CG37. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/page.aspx?o=345136 [accessed July 2006].
Nicholson 1985
-
- Nicholson WL. Cracked nipples in breast feeding mothers: a randomised trial of three methods of management. Nursing Mothers Association of Australia 1985;21(4):7‐10.
Owen 2008
-
- Owen CG, Whincup PH, Kaye SJ. Does initial breastfeeding lead to lower blood cholesterol in adult life? A quantitative review of the evidence. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;88(2):305‐14. - PubMed
Paradise 1994
-
- Paradise J, Elster B, Tan L. Evidence in infants with cleft palate that breast milk protects against otitis media. Pediatrics 1994;94:853‐86. - PubMed
Patel 2013
Pettit 1997
-
- Pettit D, Forman M, Hanson R, Knowler W, Bennett P. Breastfeeding and the incidence of non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. Lancet 1997;350:166‐8. - PubMed
Picciano 1984
-
- Picciano MF. What constitutes a representative human milk sample?. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1984;3(2):280‐3. - PubMed
Qi 2014
-
- Qi Y, Zhang Y, Fein S, Wang C, Loyo‐Berríos N. Maternal and beast pump factors associated with breast pump problems and injuries. Journal of Human Lactation 2014;30:62‐72. - PubMed
Quigley 2007
-
- Quigley MA, Kelly YJ, Sacker A. Breastfeeding and hospitalization for diarrheal and respiratory infection in the United Kingdom Millennium Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2007;119:e837‐e842. - PubMed
RevMan 2003 [Computer program]
-
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 4.2 for Windows. Oxford, England: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2003.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ryan 2013
-
- Ryan K, Smith L, Alexander J. When baby's chronic illness and disability interfere with breastfeeding: women's emotional adjustment. Midwifery 2013;29(7):794‐800. - PubMed
Schanler 1999
-
- Schanler RJ, Shulman RJ, Lau C. Feeding strategies for premature infants: beneficial outcomes of feeding fortified human milk versus preterm formula. Pediatrics 1999;103(6):1150‐7. - PubMed
Schwartz 2002
-
- Schwartz K, D'Arcy H, Gillespie B, Bobo J, Longeway M, Foxman B. Factors associated with weaning in the first 3 months postpartum. Journal of Family Practice 2002;51:439‐44. - PubMed
Spencer 1981
Sponsel 1983
Tengku 2012
Upadhyay 2004
-
- Upadhyay A, Aggarwal R, Narayan S, Joshi M, Paul VK, Deorari A. Analgesic effect of expressed breast milk in procedural pain in term neonates: a randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind trial. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 2004;93(4):518‐22. - PubMed
Victora 1987
-
- Victora C, Smith P, Vaughn J, Nobre L, Lombardi C, Teixeira A, et al. Evidence for protection by breastfeeding against infant deaths from infectious diseases in Brazil. Lancet 1987;1:319‐21. - PubMed
Wennergren 1985
-
- Wennergren M, Wiqvist N, Wennergren G. Manual breast pumps promote successful breast feeding. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1985;64(8):673‐5. - PubMed
WHO 2002
-
- WHO. Global strategy on infant and young child feeding. Executive Board paper. Report No.:EB 109/12. Geneva: WHO, 2002.
WHO/UNICEF 1989
-
- WHO/UNICEF. Protecting, promoting and supporting breastfeeding: the special role of the maternity services. Geneva: WHO, 1989.
Widdows 1933
Wilde 1995
-
- Wilde CJ, Prentice A, Peaker M. Breastfeeding: matching supply with demand in human lactation. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 1995;54:401‐6. - PubMed
Williams 1989
-
- Williams J, Auerbach KG, Jacobi A. Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) in breastfeeding mothers. Clinical Pediatrics 1989;28:42‐3.
Win 2006
Zoppou 1997
-
- Zoppou C, Barry SI, Mercer GN. Comparing breastfeeding and breast pumps using a computer model. Journal of Human Lactation 1997;13(3):195‐202. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Becker 2006
Becker 2008
Becker 2011
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

